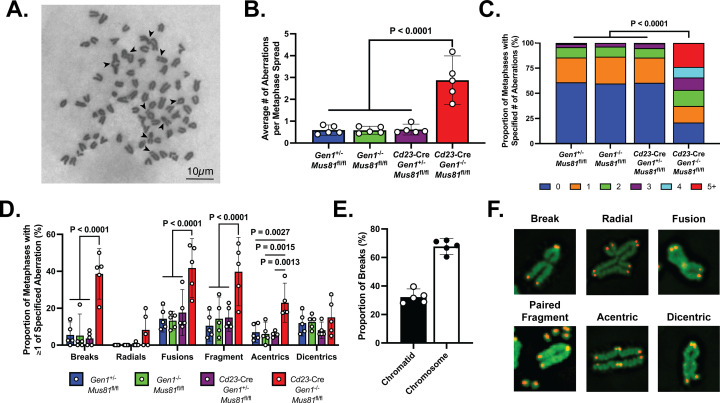
Figure 5. Metaphase chromosomal analysis of activated DKO B cells.
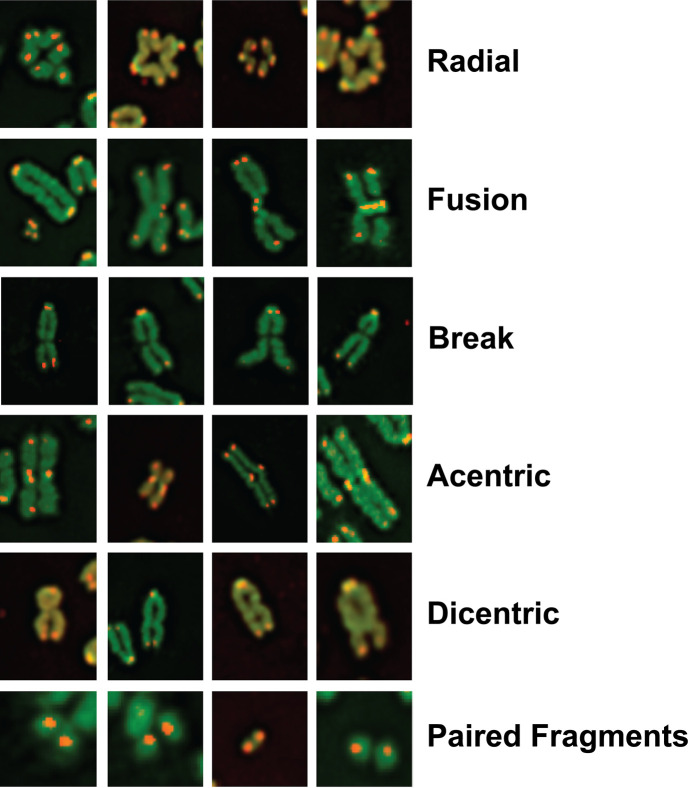
(A) Representative image of a DKO metaphase spread with arrows indicating chromosomal breaks, fragments, and fusions in metaphases of activated DKO B cells. (B) Quantification of the average number of chromosomal aberrations across 45–50 metaphase spreads prepared from each B cell culture. (C) Percentage breakdown of metaphases exhibiting 0 to greater than 5 chromosomal aberrations. (D) Fraction of metaphases containing the indicated types of chromosomal abnormalities. Total percentage per genotype exceeds 100% as some metaphases exhibit more than one type of abnormality. (E) Proportion of chromatid and chromosome breaks among the 163 breaks observed in DKO metaphase spreads exhibiting at least one break. (F) Tel-FISH images of DKO metaphases highlighting the proximal location of the chromosomal damage to the telomeres. Note that the events labeled as dicentrics here and in Figure 5—figure supplement 1 may include chromosomes with residual cohesins remaining at a repaired DSB and those with condensins that persist after loading onto the chromosomal arms during mitotic entry. Data in (B–E) are from three independent experiments with 5 mice (totaling between 215 and 235 metaphase spreads) per genotype. For (C), the percentages are the average of the data combined from all five mice. Bars display the arithmetic mean and error bars represent the 95% confidence interval of the measured parameters. P values were computed with ordinary one-way ANOVA analysis (B, D) and the Kruskal-Wallis test (C) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test without pairing. Means of all groups were compared to that of Cd23-Cre Gen1−/− Mus81fl/fl.