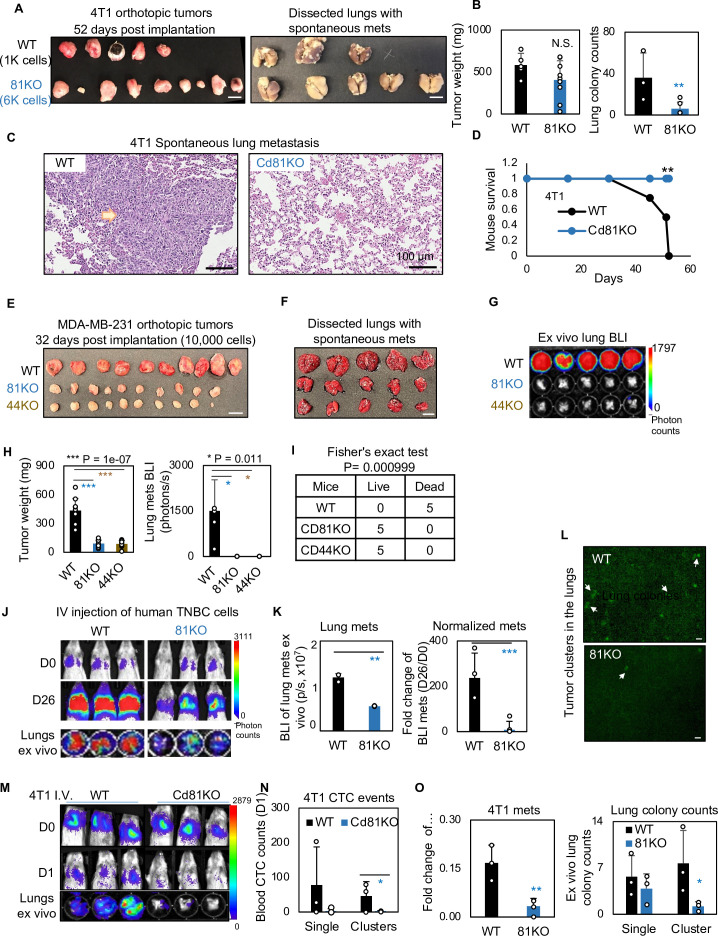
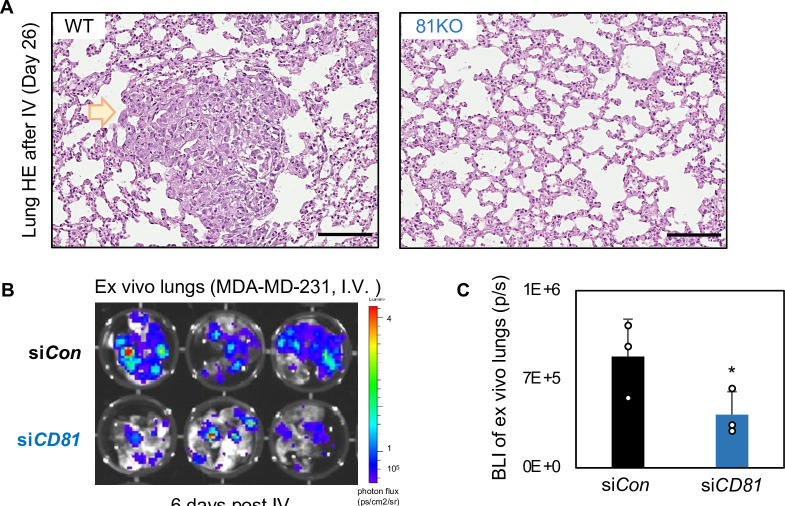
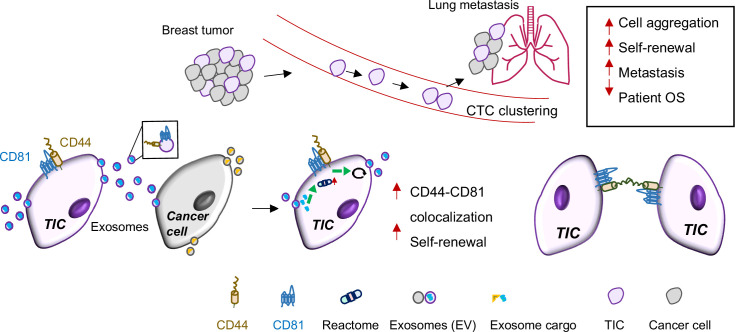
Figure 6. CD81 deficiency abrogates lung metastasis in breast cancer.
(A) Photos of 4T1 orthotopic tumors (left panels) grown from implantations of comparable (1000) WT and (6000) Cd81KO cells into the L4/R4 mammary fat pads (N = 5 Balb/c mice with 10 injections) and the fixed lungs with overt metastatic colonies. By the terminal day 52, two mice from the WT group died and the left three were sick and sacrificed. Scale bar = 1 cm. (B) Bar graph of the tumor weights and lung colonies count between the WT tumors and KO tumors. (C) IHC (HE) images of lung colonies from the WT group mice (a higher number of visible lung metastases at a larger size) as compared to the Cd81 KO group. Scale bar = 100 µm. N.S. = not significant, two-tailed Student T-test **p = 0.01 (n = 5 mice). Error bars represent standard deviation. . (D) Distinct mouse survival between 4T1 WT and Cd81 KO tumor bearing mice with spontaneous lung metastases. Two-tailed Student T-test **p = 0.01 (n = 5 mice). Photos of WT and 81KO MDA-MB-231 orthotopic tumors (E) grown from 10,000 cell implantations and dissected mouse lungs on day 32 (F) (N = 5 NSG mice with 10 injections) Scale bar = 1 cm. Error bars represent standard deviation. (G) BLI images and of spontaneous metastases in the lungs ex vivo following after orthotopic implantation of WT and 81KO MDA-MB-231 cells into NSG mice. Error bars represent standard deviation. *p = 0.011 (n = 5 mice). (H) Quantification of tumor weights, lung metastases, and relative metastatic burden normalized by tumor weight. Error bars represent standard deviation. Two-tailed Student T-test was used. ***p = 1e−07, *p = 0.011. (I) Table of mouse mortality or survival by day 32 after orthotopic implantation. Three mice from the WT group died and the left two were sick and sacrificed whereas the 81KO tumor-bearing mice would have survived. Fisher’s test was used **p = 0.01 (n = 5). (J) BLI images of lung colonization following the tail vein injections of MDA-MB-231 WT and 81KO cells into NSG mice on days 0 and 26. The bottom row shows dissected lungs ex vivo. (K) Quantified BLI signals (left panel) and normalized metastasis intensity (relative to the day 0 signals) of MDA-MB-231 cells in the dissected lungs ex vivo on day 26 after tail vein injections. Error bars represent standard deviation. Two-tailed Student T-test **p < 0.007. ***p = 0.001 (N = 3 mice). (L) Representative fluorescence images (top two panels) of mouse lungs and quantified metastatic colonies (singles and clustered, bottom panel) of WT and CD81KO L2G+ MDA-MB-231 cells (D26). Scale bar = 100 mm. Error bars represent standard deviation. Two-tailed Student T-test was used. *p = 0.044. BLI images of mice (days 0 and 1) and dissected lungs on day 1 (M) lood circulating tumor cell (CTC) counts (L2G+ singles and clusters) measured via flow cytometry on day 1 (N), and relative lung metastasis via BLI on day 1 (O, relative to day 0) following the tail vein injections of 4T1-WT and Cd81KO cells into Babl/c mice (N = 3), *p = 0.047, **p = 0.007. Error bars represent standard deviation. Two-tailed Student T-test was used. These experiments were repeated at least twice to show consistent conclusions.