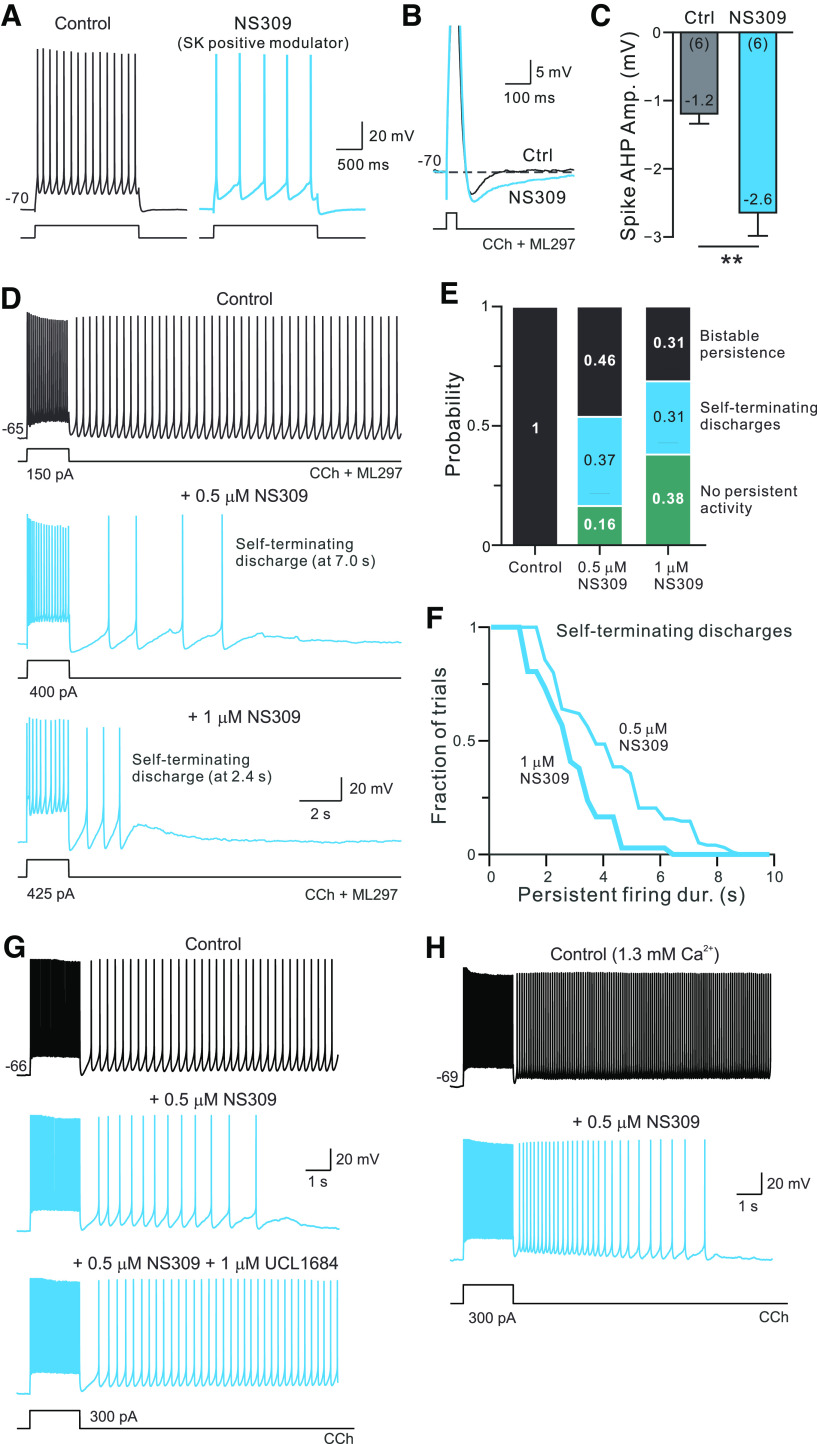
Figure 4.
Pharmacologically enhancing SK currents converts bistable persistent firing into self-terminating discharges. A, Enhancing SK currents with NS309 (blue trace) decreased the step-evoked firing rate from control conditions (black). B, Enhancing SK currents with NS309 also increased spike AHP amplitude and slowed AHP kinetics. Horizontal dashed line at membrane potential before depolarizing pulse stimulus that triggered the AP. Action potentials were truncated. C, Summary of spike AHP amplitude before (Ctrl) and after NS309. **p = 0.016, T = 3.58, df = 5; paired t test. D, Low concentrations of NS309 (0.5–1 μm) convert bistable persistent firing responses into self-terminating discharges. Example self-terminating discharge responses recorded with 0.5 μm (middle panel, same cell as control trace) and 1 μm NS309 (different cell). Stimulus amplitude increased in NS309 traces to compensate for reduction in step-evoked firing frequency. E, Summary of persistent firing response dynamics in control experiments without NS309 and following bath application of 0.5 or 1 μm NS309 (middle and right bars, respectively). Response types categorized as either bistable (persistent firing for >10 s following stimulus offset; black), discharges that spontaneously terminated within 10 s (blue), or trials with no spiking following stimulus (teal). F, Summary of the duration of self-terminating discharges triggered in either 0.5 μm (thin line; N = 29 trials) or 1 μm NS309 (thick line; N = 22 trials). The two distributions are statistically different (p < 0.015, d = 0.357; K-S test). G, Ability of NS309 to promote self-terminating discharges is reversed by the SK channel blocker UCL1684 (1 μm; bottom trace). Blue traces indicate responses recorded with 0.5 μm NS309 present. H, The SK modulator NS309 promotes self-terminating firing in ACSF containing 1.3 mm Ca2+. Control and NS309 conditions include 4 μm CCh.