Figure 5.
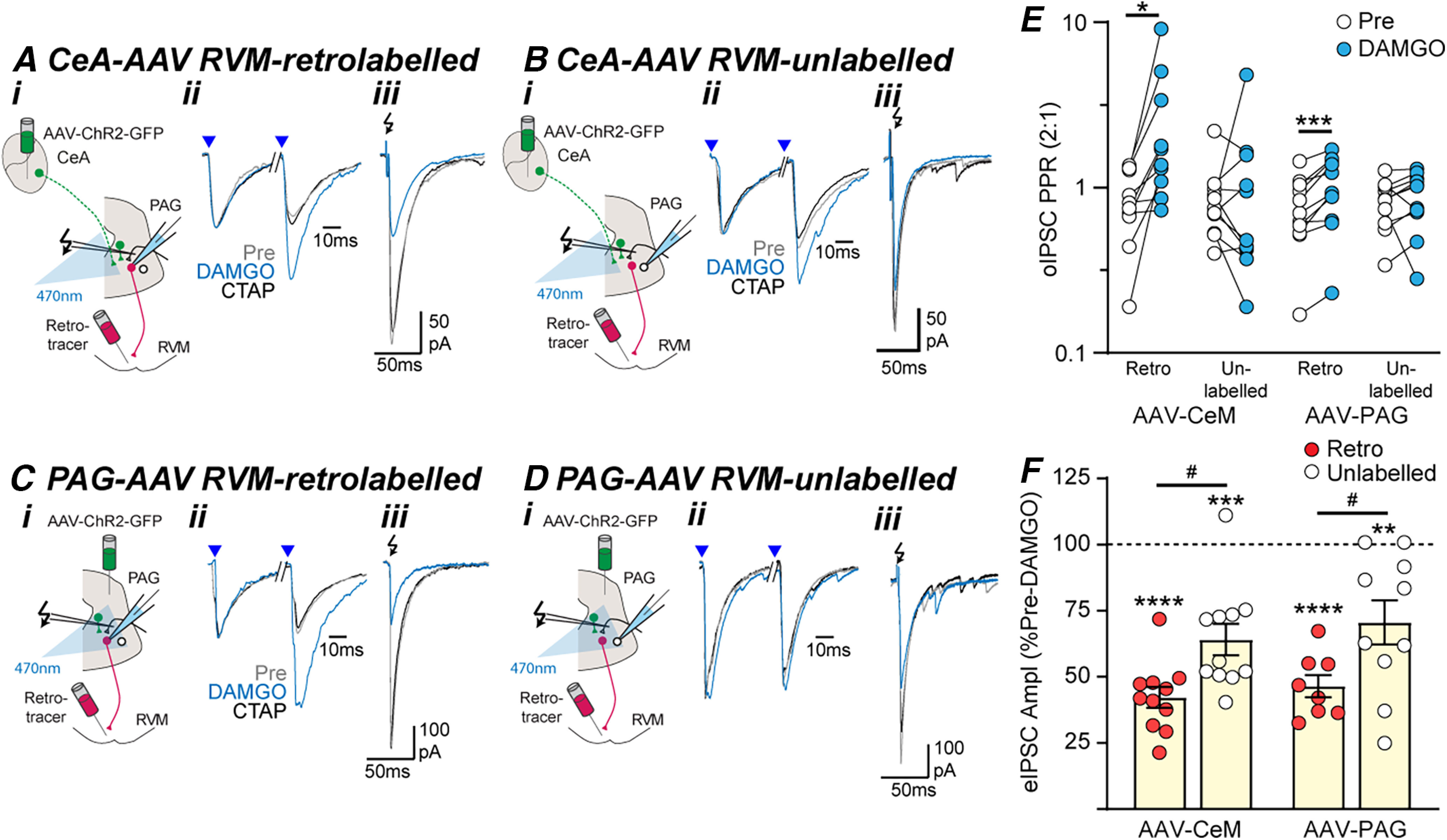
Opioid inhibition of GABAergic inputs onto PAG output neurons is presynaptic. Effect of DAMGO and CTAP on optically and electrically evoked IPSCs (oIPSCs, eIPSCs) in (A, C) RVM-retrolabeled and (B, D) unlabeled PAG neurons from (A, B) intra-CeA and (C, D) intra-PAG AAV-ChR2-injected animals. In panels A–D, (i) the experiment configuration in animals with an intra-RVM retrograde tracer injection plus and intra-CeA, or PAG AAV-ChR2 injection; (ii) averaged traces of paired optically evoked IPSCs (blue arrows) normalized to the first IPSC; (iii) and electrically (black arrows) evoked IPSCs (from the corresponding neurons in Fig. 4A–D). Scatter plots of the effect of DAMGO on (E) the paired-pulse ratio of oIPSCs and (F) the amplitude of eIPSCs in RVM-retrolabeled and unlabeled PAG neurons from intra-CeA and intra-PAG AAV-ChR2-injected animals. In E, F, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (pre vs DAMGO, paired t tests). In F, #p < 0.05 (post hoc Sidak comparisons).
