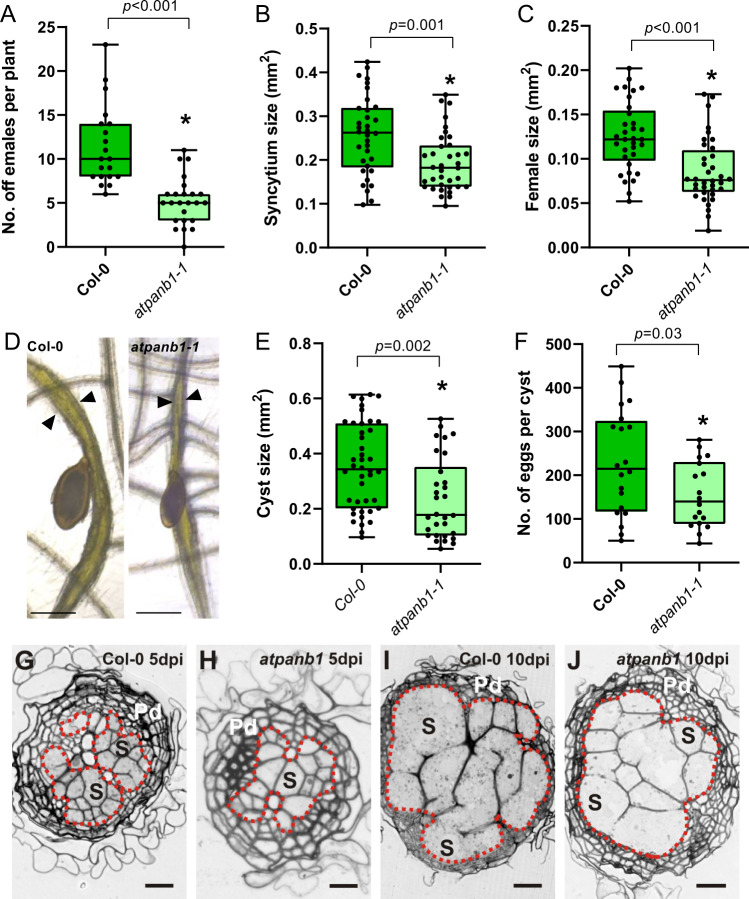
Fig. 7. AtPANB1 is required for cyst nematode parasitism.
A Number of female cyst nematodes present per plant root system at 14 dpi (Col-0, n = 20; atpanb1-1, n = 24). B Size of syncytia at 14 dpi. Female-associated syncytia were randomly selected and their outlines were measured (Col-0, n = 33; atpanb1-1, n = 36). C Size of female nematodes at 14 dpi. Female cyst nematodes were randomly selected and their outlines were measured (Col-0, n = 33; atpanb1-1, n = 36). D Example images of nematode infection on Col-0 and atpanb1-1 mutants. Arrowheads indicate syncytium boundaries and asterisks indicate female nematodes. E Size of cysts at 42 dpi. Nematode cysts were randomly selected and their outlines were measured (Col-0, n = 43; atpanb1-1, n = 32). F Number of eggs per cyst at 42 dpi. Cysts were randomly selected and their egg numbers were counted (Col-0, n = 20; atpanb1-1, n = 19). A–C, E, F). Experiments were performed 3–8 times independently with a similar outcome. Data from one experiment is shown. Data were analysed using Student’s t test (two-sided; α = 0.05) and asterisks indicate significantly different means. For box plots, centre line is median; box limits are upper and lower quartiles; whiskers are minimum and maximum value; points are all individual values superimposed on graphs. Source data are provided as a source data file. G–J Light microscopy images of cross sections taken through the widest part of syncytia induced by H. schachtii in Col-0 (G, I) and atpanb1-1 (H, J) roots at 5 (G, H) and 10 dpi (I, J). Syncytial elements and neighbouring enlarged cells presumably undergoing transition into syncytial elements are outlined with red dotted lines. Pd periderm, S example (not all) cells contributing to the syncytium. Scale bars: 20 µm.