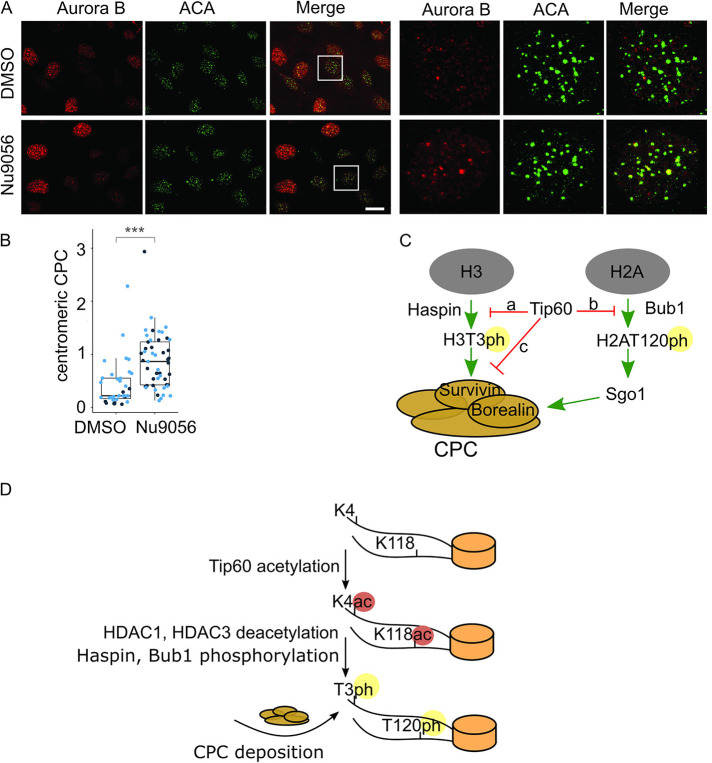
FIGURE 6:
Inhibition of Tip60 promotes premature centromeric targeting of Aurora B in interphase cells. (A) Inhibition of Tip60 by Nu9056 leads to Aurora B localization at centromeres in interphase (S/G2) cells as shown by immunofluorescence; scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Quantification of S/G2 centromeric fluorescence signals for Aurora B in control cells (n = 9, 26) and in Tip60-inhibited cells (n = 26, 23) p value (2.833⋅10–7, 8.152⋅10–5). Aurora B signal that overlaps with an ACA mask was quantified in S/G2 cells as defined by Aurora B signal. G1 cells have low Aurora B signal since Aurora B is an APC substrate. For statistical analysis Welch’s t test was applied. ***P < 0.001. (C) A proposed model for Aurora B localization regulated by acetylation of H3K4 of H3 by Tip60. Our data suggest that histone H3K4ac by Tip60 during S/G2 prevents Haspin phosphorylation of H3T3 (arrow a) and Survivin binding to chromatin to inhibit CPC localization to centromeres (arrow c). During the middle of prophase HDAC3 removes H3K4ac mark to enable CPC accumulation at inner centromeres. Previous studies have shown that Tip60 inhibits Bub1 binding to H2AT120 (arrow b) (Lee et al., 2018) and together with our work it suggests that Tip60 is a master regulator of CPC localization. (D) A model to control the timing of CPC localization to inner centromeres through changes in chromatin PTMs. Tip60 acetylates histone H3 on K4 and histone H2A on K118 in S/G2 to prevent CPC localization. In midprophase HDAC1 and HDAC3 deacetylate these histone marks to enable Bub1 phosphorylation and subsequent Sgo1 recruitment, Haspin phosphorylation of histone H3T3 and subsequent Survivin binding of H3T3ph. Together these events drive CPC recruitment to inner centromeres in midprophase.