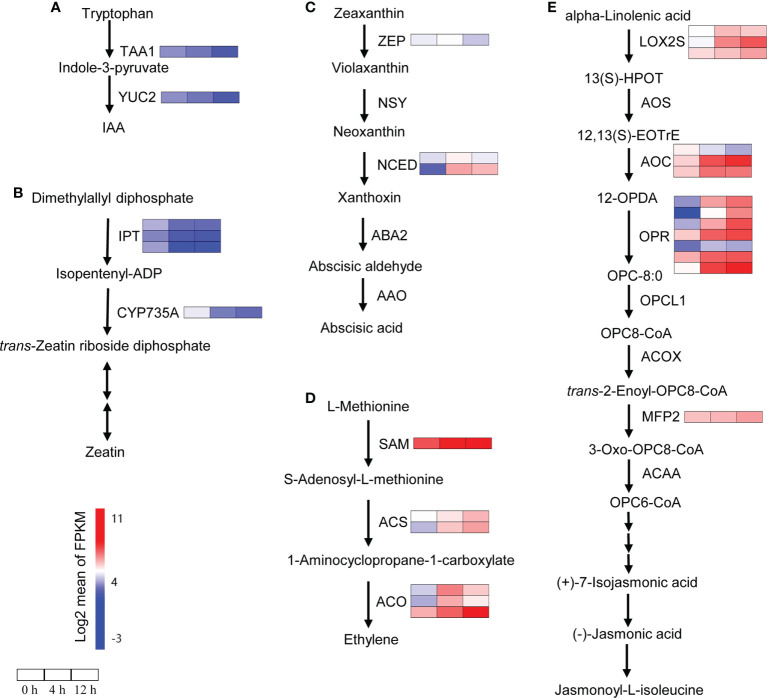
Figure 3.
Changes in the expression of biosynthetic genes encoding phytohormones after salt stress. (A) Expression analysis of IAA biosynthetic genes. IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; TAA, tryptophan aminotransferase of Arabidopsis; YUC, indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase 2. (B) Expression analysis of zeatin biosynthetic genes. IPT, isopentenyltransferase; CYP735A, cytokinin trans-hydroxylase. (C) Expression analysis of ABA biosynthetic genes. ABA, abscisic acid; ZEP, zeaxanthin epoxidase; NSY, neoxanthin synthase; NCED, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase; ABA2, xanthoxin dehydrogenase; AAO, abscisic-aldehyde oxidase. (D) Expression analysis of ethylene biosynthetic genes. SAM, S-adenosylmethionine synthetase; ACS, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase; ACO, aminocyclopropanecarboxylate oxidase. (E) Expression analysis of JA biosynthetic genes. LOX2S, lipoxygenase; AOS, hydroperoxide dehydratase; AOC, allene oxide cyclase; OPR, 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductase; OPCL1, OPC-8:0 CoA ligase 1; ACX, acyl-CoA oxidase; MFP2, enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase 2; ACAA, acetyl-CoA acyltransferase. Genes that changed significantly at least one time point after salt treatment are shown. Red indicates high expression and blue indicates low expression.