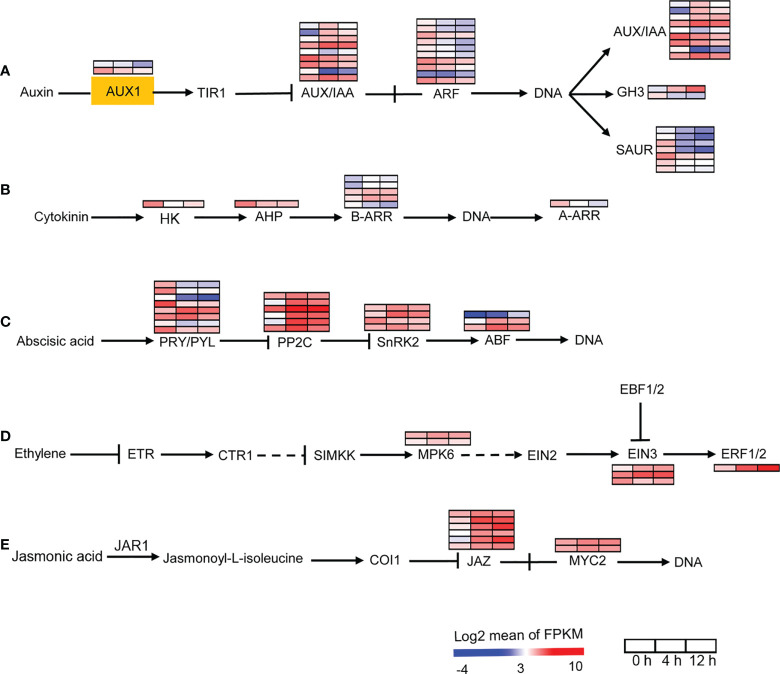
Figure 4.
Changes in the expression of plant hormone signal transduction pathway under salt treatment. (A) Expression analysis of auxin signal transduction pathway genes. AUX1, auxin influx carrier 1; TIR1, transport inhibitor response 1; Aux/IAA, auxin/indole acetic acid protein; ARF, auxin response factor; GH3, Gretchen Hagen; SAUR, small auxin-up RNAs. (B) Expression analysis of cytokinin signal transduction pathway genes. HK, histidine kinase; AHP, histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein; A-ARR, type‐A Arabidopsis response regulator; B-ARR, type‐B Arabidopsis response regulator. (C) Expression analysis of ABA signal transduction pathway genes. PRY/PRL, abscisic acid receptor PYR/PYL family; PPC2C, protein phosphatase-2C; SnRK2, SNF1‐related protein kinase 2, ABF, ABA responsive element binding factor. (D) Expression analysis of ethylene signal transduction pathway genes. ETR, ethylene receptor; CTR1, serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; SIMKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MPK6, mitogen-activated protein kinase 6; EIN2/3, ethylene-insensitive protein 2/3; EBF1/2, EIN3‐binding F‐box protein 1/2; ERF1/2, ethylene-responsive transcription factor 1/2. (E) Expression analysis of JA signal transduction pathway genes. JAR1, jasmonic acid-amino synthetase; COI1, coronatine-insensitive protein 1, MYC2, transcription factor MYC2. The pathways were redraw based on ‘Plant hormone signal transduction’ in the KEGG database (https://www.kegg.jp/). Genes that changed significantly in at least one time point after salt treatment are shown.