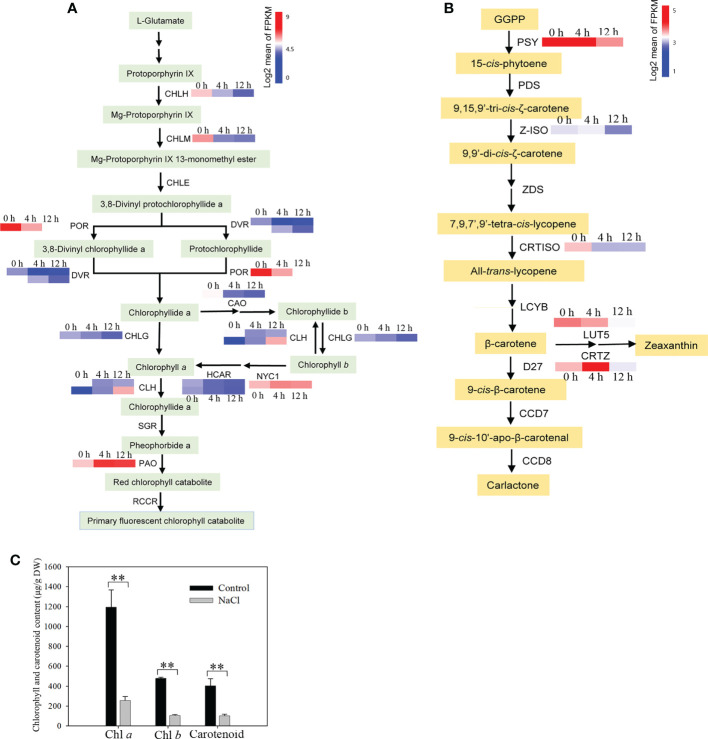
Figure 6.
Analysis of the content of photosynthetic pigments and their metabolic pathway genes after salt treatment. (A) Analysis of expression of genes related to the Chl metabolic pathway. CHLH, magnesium chelatase subunit H; CHLM, magnesium-protoporphyrin O-methyltransferase; CHLE, magnesium-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (oxidative) cyclase; POR, protochlorophyllide reductase; DVR, divinyl chlorophyllide a 8-vinyl-reductase; CHLG, chlorophyll/bacteriochlorophyll a synthase; CAO, chlorophyllide a oxygenase; CLH, chlorophyllase; NYC1, chlorophyll(ide) b reductase 1; HCAR, 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll a reductase; SGR, magnesium dechelatase; PAO, pheophorbide a oxygenase; RCCR, red chlorophyll catabolite reductase. (B) Changes in carotenoid biosynthetic pathway genes in response to salt stress. GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; PSY, 15-cis-phytoene synthase; PDS, 15-cis-phytoene desaturase; Z-ISO, ζ-carotene isomerase; ZDS, ζ-carotene desaturase; CRTISO, carotene cis-trans isomerase; LCYB, lycopene β-cyclase; LUT5, β-ring hydroxylase; CRTZ, β-carotene 3-hydroxylase; D27, β-carotene isomerase; CCD7, 9-cis-β-carotene 9’,10’-cleaving dioxygenase; CCD8, carlactone synthase/all-trans-10’-apo-β-carotenal 13,14-cleaving dioxygenase. The Chl metabolic pathway and carotenoid biosynthetic pathway were redrawn based on ‘porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism’ and ‘carotenoid biosynthesis’ pathways in the KEGG database (https://www.kegg.jp/). Genes whose expression changed significantly in at least one time point after salt treatment are shown. (C) Content of chlorophyll (Chl) a, Chl b and carotenoids. Roots were harvested from plantlets after 250 mM NaCl treatment for two weeks. Bars indicate means ± standard deviation of three replicates. ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01 according to the Dunnett test. DW, dry weight.