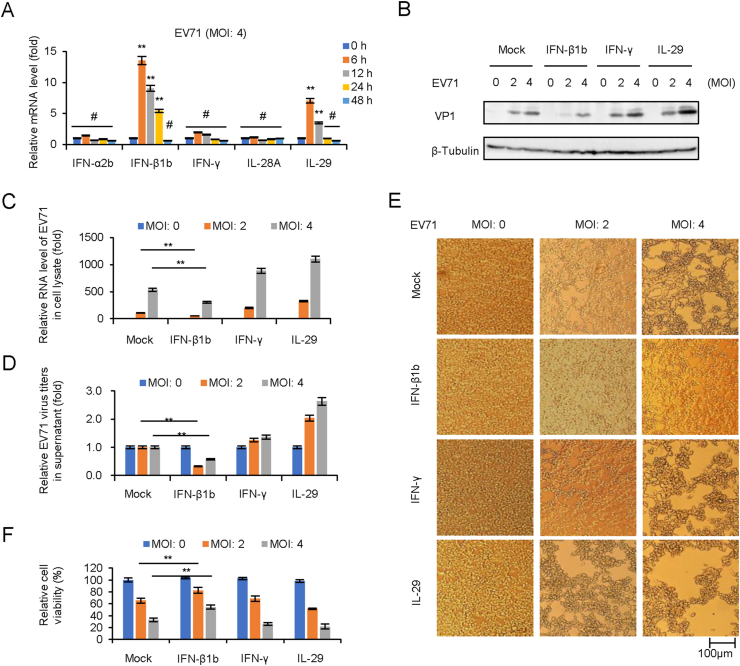
Fig. 3.
IFN-β1b significantly inhibits EV71 replication and viral cytopathic effect. A EV71 infection induces the expression of IFN-β1b in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were infected with EV71 at an MOI of 4, and the expression levels of IFNs were examined by RT-qPCR at different time points. The RNA level of “0 h” was set as “1”. B IFN-β1b plays an antiviral effect in EV71 infected HEK293T cells. After 250 U/mL IFN-β1b, 250 U/mL IFN-γ, and 250 U/mL IL29 treated HEK293T cells for 24 h, cells were infected EV71 at different MOI. The expression levels of VP1 were examined by Western blotting. C The expression levels of EV71 viral RNA were examined by RT-qPCR. The RNA level at an MOI of 0 was set as “1”. D Viral titers in the supernatants were determined by the plaque assay. E Apparent CPE was observed at 48 h.p.i. F Cell viability in the experiment of Fig. 3E was measured by CCK8. The cell viability at an MOI of 0 was set as “1”. The results represent the means ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed using Student's t-test (# no significance, ∗∗P < 0.01).