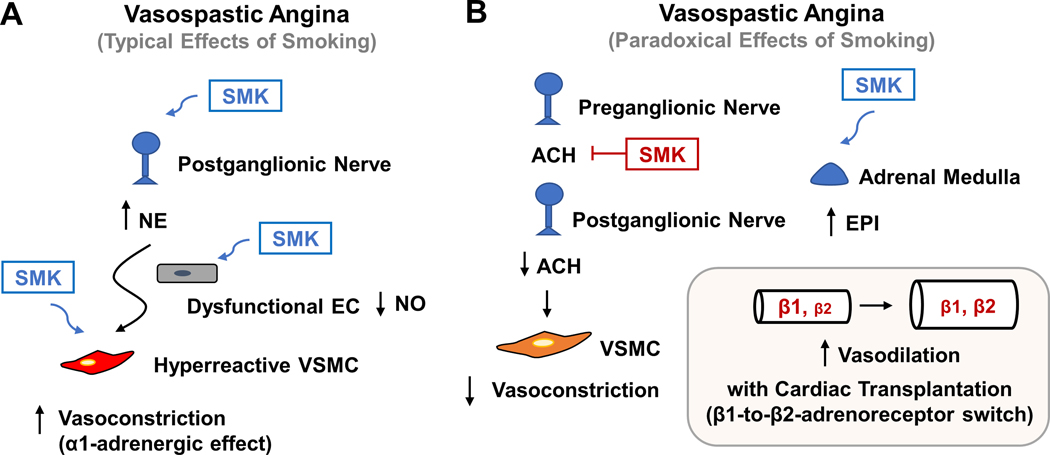
Figure 4. Schematics showing typical and paradoxical effects of smoking on vasospastic angina.
(A) Smoking (SMK) can predispose to vasospastic angina by activating the sympathetic nervous system, impair endothelial function, and make vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) more prone to contraction. (B) Very rarely, smoking can paradoxically provide relief for vasospastic angina by potentially antagonizing actetylcholine (ACH) action on the postganglionic nerve. Additionally, in the setting of cardiac transplantation, smoking or nicotine can cause an increase in the adrenal release of epinephrine (EPI), which may favor vasodilation, and thus less vasospasm, due to a β1-to-β2-adrenoreceptor switch in the transplanted heart.