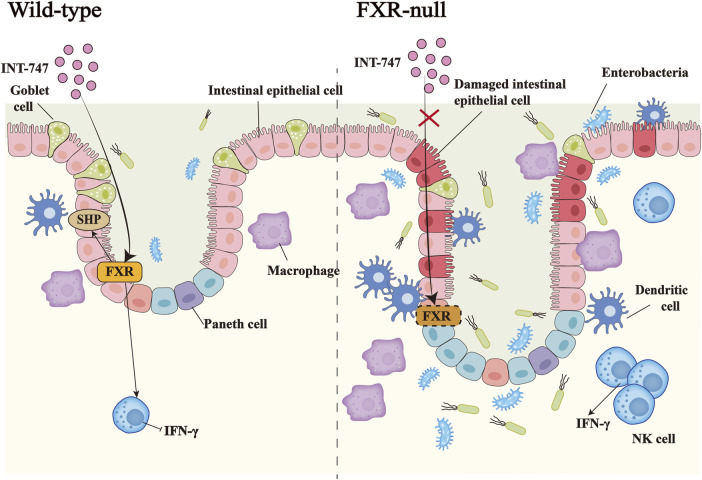
FIGURE 2.
The importance of FXR in inflammatory bowel disease. In DSS-induced IBD, the administration of the FXR agonist INT-747 to FXR-KO mice and WT mice, activates the expression of FXR in the intestinal tract of WT mice, thereby promoting the upregulation of the target gene SHP of FXR and inhibiting the release of the pro-inflammatory factor IFN-γ by NK cells. INT-747 reduced intestinal permeability in WT mice, while FXR-KO mice could not have the same phenomenon due to the loss of the FXR gene. Meanwhile, FXR-KO mice had more damaged intestinal epithelial cells, fewer goblet cells, and increased bacterial invasion. The number of dendritic cells, macrophages, NK cells, and other immune cells also increased, which led to susceptibility to bacterial translocations.