Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Overview of matching STARNET CAD cases to controls without obstructive CAD according to age, gender and BMI.
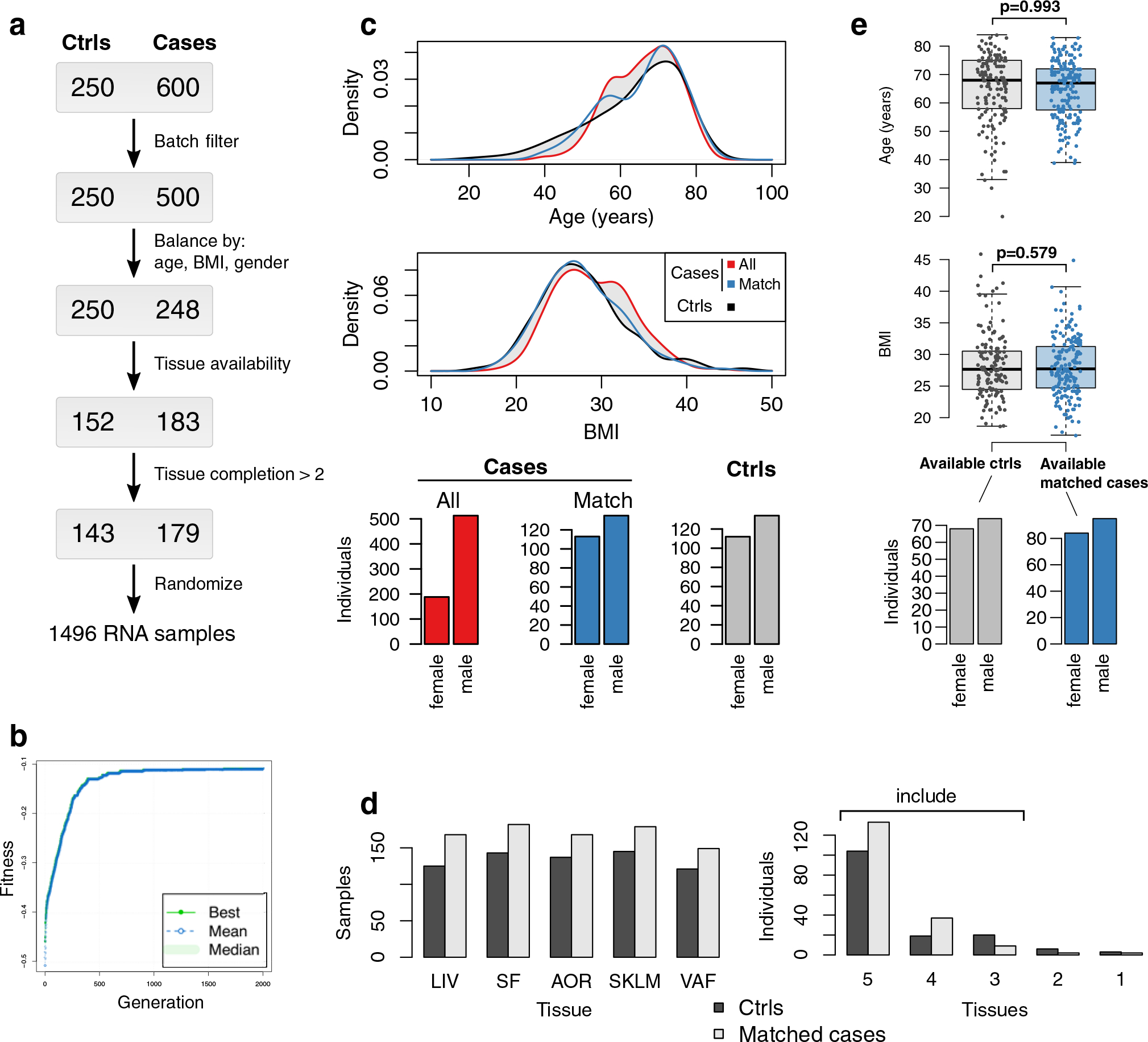
The 600 CAD cases underwent coronary artery by-pass grafting (CABG) surgery due to obstructive CAD. The 250 controls were patients eligible to open heart surgery other than CABG (mainly valve replacements) who had no signs of obstructive CAD in pre-operative angiograms (SYNTAX score =0). a, Overview of steps used to select RNA samples from the 600 CAD cases for sequencing by matching them to RNA samples available from the 250 controls according to age, gender and body mass index (BMI). b, Evolutionary algorithm optimizing an objective function quantifying the discrepancy of univariate distribution of age, BMI, and gender between selected cases and controls. c, Distribution of age and BMI (kernel probability density estimates, upper panel) and bar plots of gender for all cases, matched cases and controls (lower panel). d, Bar plots showing per-tissue sample sizes based on tissue sample availability (left panel). Only STARNET subjects in whom at least 3 tissues were sampled were included (right panel). e, Two box plots and one bar plot showing the final balances in age (upper panel) and BMI (middle panel), and gender (lower panel), respectively, between the selected CAD cases and the CAD-negative controls. Median center, lower and upper quartile box, and 1.5 interquartile range whiskers. Two-tailed t-tests.
