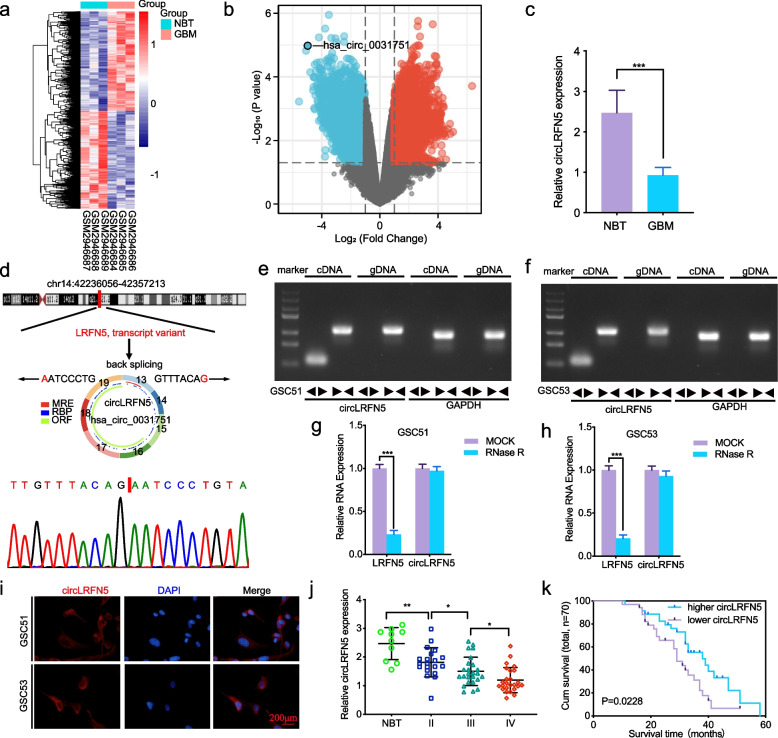
Fig. 1.
The identification and characteristics of circLRFN5 in GBM. a, b Heatmaps (a) and volcano plots (b) of circRNAs that were differentially expressed between GBM and normal brain tissues (NBT) in GSE109569. c The expression of circLRFN5 in GBM tissues and NBT as measured by qPCR. d Schematic illustration of the genomic location, circular structure exon composition and back splicing site of circLRFN5. The back-splicing site of circLRFN5 was validated by Sanger sequencing. e, f Agarose gel electrophoresis showed the expression of circLRFN5 in cDNA and gDNA samples from GSC51 (e) and GSC53 (f) using divergent and convergent primers. β-actin served as a linear RNA control. g, h RNase treatment was used to evaluate the stability of circLRFN5 and LRFN5 mRNA in GSC51 (g) and GSC53 (h). i FISH assays showed the cellular localization of circLRFN5 in GSC51 and GSC53 cells. Scale bar = 200 μm. j The expression of circLRFN5 in 70 different WHO-grade glioma tissues as measured by qPCR. k The survival prognosis in different circLRFN5 expression groups was detected in 70 glioma patients. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (three independent experiments). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001