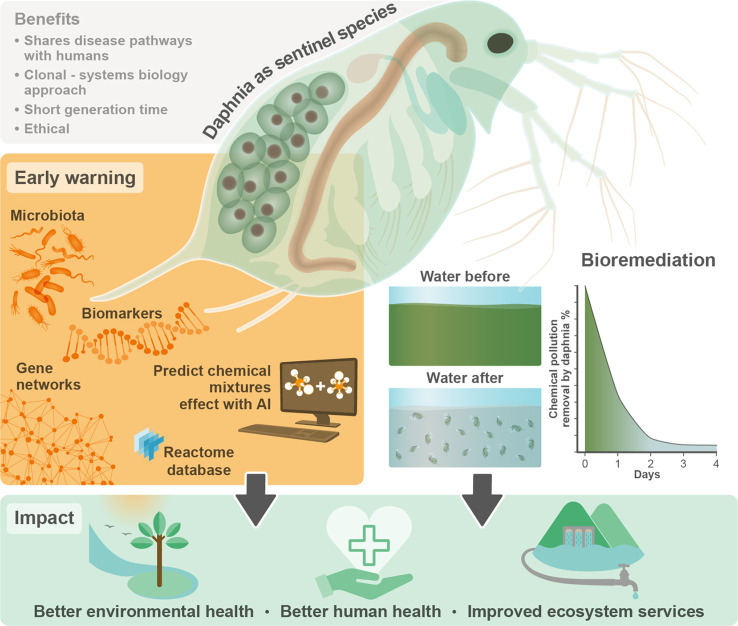
Figure 1.
Daphnia as an early warning and remedial system. In the proposed framework, the sentinel species Daphnia is used both as an early warning system and as a bioremediation tool for chemical pollution. Daphnia clonality enables the synchronous analysis of ecological and molecular perturbations by environmental pollution (early warning). This enables the establishment of associations between sublethal doses of chemicals within mixtures and molecular biomarkers. Using the manually curated Reactome database, gene ontologies and conserved molecular functions can be identified in responsive modules across organisms, including humans. Once chemicals have entered the environment, remedial actions are needed. The sentinel species Daphnia has the potential to become a sustainable bioremediation agent as it removes excess nutrients from water, preventing eutrophication, and a wide range of persistent chemicals (bioremediation). By using Daphnia as a diagnostic and remedial agent, adverse effects for humans and the environment can be significantly reduced (impact).