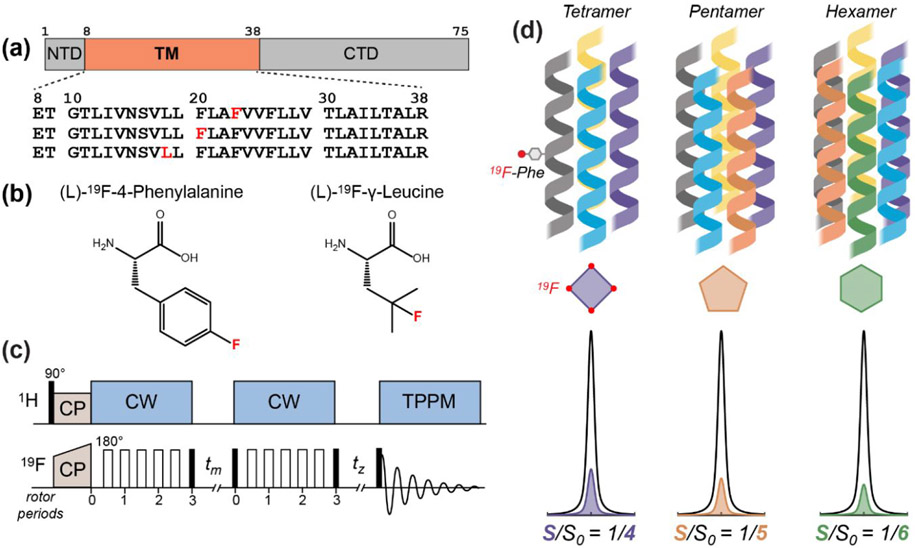
Figure 1.
The 19F solid-state NMR approach for determining the stoichiometry of ETM assembly in lipid bilayers. (a) Amino acid sequence diagram of the SARS-CoV-2 E protein. The transmembrane (TM) domain is preceded by a short N-terminal domain (NTD) and is followed by a C-terminal domain (CTD). The amino acid sequences of singly fluorinated ETM peptides used in this study are shown. (b) Structures of the 4-19F-phenylalanine and 19F-Cγ-leucine that are synthetically incorporated into the ETM peptide. (c) Pulse sequence of the 19F CODEX experiment. Filled and open rectangles designate 90° and 180° pulses, respectively. CP: cross-polarization; CW continuous-wave heteronuclear decoupling; TPPM, two-phase modulation heteronuclear decoupling. 19F spin diffusion during the mixing time tm reduces the intensity of a 19F spin echo. The CODEX dephased (S) experiment has a long tm and a short tz, while the CODEX control (S0) experiment has a short tm and a long tz. The sum of the two mixing times is the same between S and S0. (d) Schematic of different stoichiometries of the ETM oligomer in the lipid membrane, with corresponding relative intensities of the CODEX S0 and S spectra.