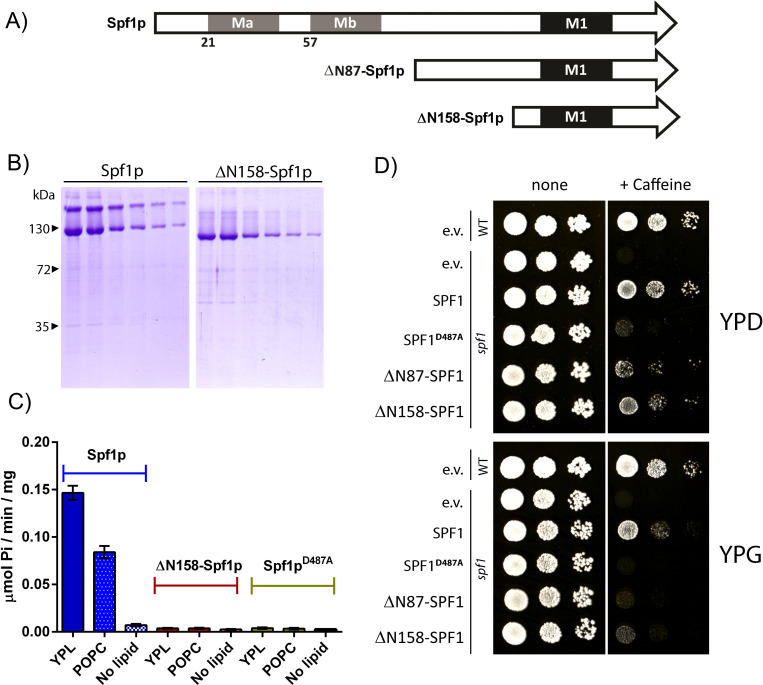
Fig 4. Viability of Spf1p and N-terminally truncated Spf1p.
A) Schematic overview of N-terminal truncations performed by genetically removing the genetic sequence that codes for the first 87 and 157 amino acids of the expression construct. Ma, Mb and TM1 is indicated in accordance with [3, 20]. B) SDS-PAGE showing the eluates for the purified fractions of the full-length expression construct (Spf1p) and the N-terminally truncated expression construct (ΔN187-Spf1p). C) ATPase activity measured for full-length (Spf1p), N-terminally truncated expression construct (ΔN187-Spf1p) and a dead control (Spf1p-D487A) after re-lipidation in mixed lipid/detergent micelles using OG as detergent (YPL, POPC) or with no lipids added. D) Complementation in spf1 deletant cells using the same expression constructs. The catalytic dead mutation D487A and the empty vector is used as a control. Complementation was tested on 10 mM caffeine plates as described in [12]. Plates grown on glucose (YPD) repression of the promotor allows survival of cells expressing the N-terminally truncated version of SPF1, but high expression conditions on galactose (YPG) hinders survival.