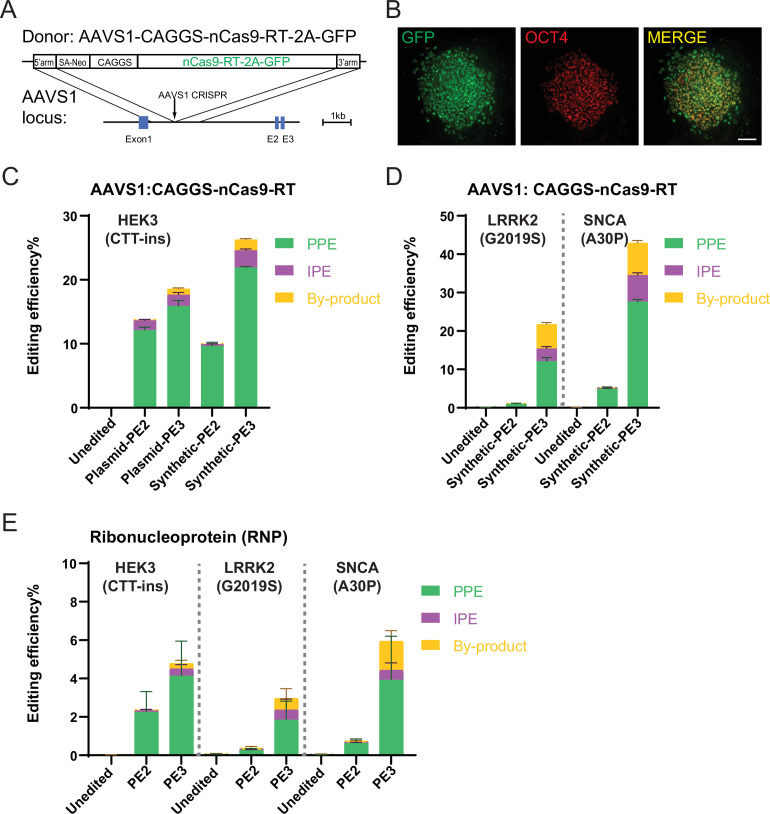
Figure 2. Prime editing (PE) in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) expressing Cas9-nickase fused to a reverse transcriptase (nCas9-RT) protein from the AAVS1 safe harbor or delivered as RNP.
(A) Schematic of the genome editing strategy to knock-in nCas9-RT-2A-GFP (PE2 version of the prime editor protein as described in Anzalone et al., 2019) into the AAVS1 locus. (B) Expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) and immunostaining of OCT4 on hESCs with nCas9-RT-2A-GFP knock-in. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Comparison of bulk PE outcomes between plasmid-expressed PE guide RNAs (pegRNAs)/nicking guide RNAs (ngRNAs) and synthetic pegRNAs/ngRNAs on HEK3 (CTT-insertion) edits in hESCs with nCas9-RT-2A-GFP knock-in. N=3. (D) Bulk PE outcomes on leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2; G2019S) and α-Synuclein (SNCA; A30P) edits using synthetic pegRNAs/ngRNAs in hESCs with nCas9-RT-2A-GFP knock-in. N=3. (E) Bulk PE outcomes from RNP delivery on HEK3 (CTT-insertion), LRRK2 (G2019S), and SNCA (A30P) edits in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). N=6. (Error bars indicate the SD, N=number of biological replicates).
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Pluripotent marker staining of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) expressing Cas9-nickase fused to a reverse transcriptase (nCas9-RT) protein from the AAVS1 safe harbor locus.
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Quality control and parameter testing of RNP-based prime editing (PE).