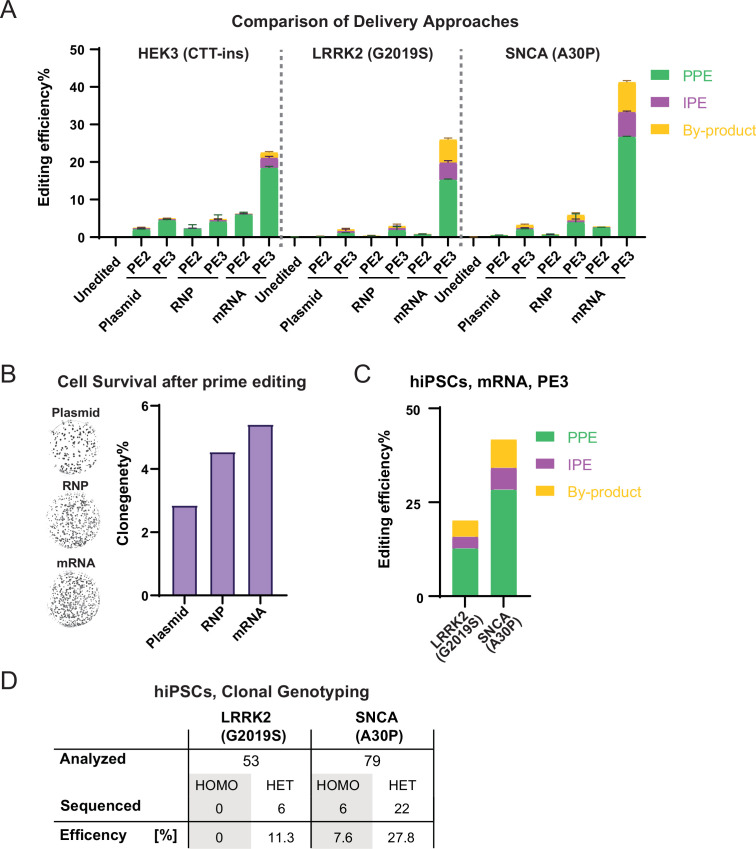
Figure 3. Highly efficient prime editing (PE) in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) using mRNA-based delivery.
(A) Comparison of bulk PE outcomes between plasmid, RNP, and mRNA-based delivery on indicated modifications in hESCs. Plasmid, mRNA groups, N=3; RNP data shown in Figure 2E was included in this analysis for direct comparison, N=6. (B) Representative images and quantification of alkaline phosphatase staining comparing clonogenicity of hESCs after nucleofection between plasmid, RNP, and mRNA-based delivery. N=2. (C) Bulk PE outcomes on leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2; G2019S) and α-Synuclein (SNCA; A30P) edits in a human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) line using mRNA-based delivery. N=2. (D) A summary of clonal genotyping from LRRK2 (G2019S) and SNCA (A30P) PE in hiPSCs indicating the number and editing efficiency of single cell-derived clones carrying the correct heterozygous (HET) or homozygous (HOMO) substitution. (N=number of biological replicates, Error bars indicate the SD for samples N>2).