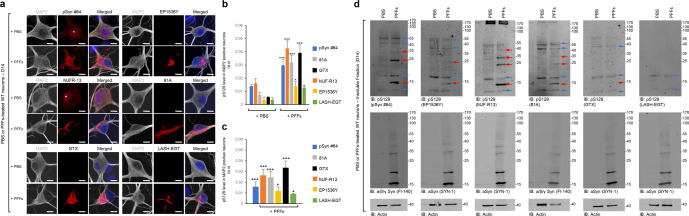
Fig. 4. Assessment of pS129 antibodies detection in the PFFs-seeded WT primary hippocampal neurons.
After 14 days of treatment with 70 nM of mouse aSyn PFFs or PBS buffer (negative control), primary hippocampal neurons were fixed or lysed, and ICC (a–c) or WB (d) analyses were performed using pS129 antibodies (pSyn#64, MJF-R13, 81A, EP1536Y, and GTX or LASH-EGT). a–c Newly formed fibrils were detected by confocal imaging (a) and quantified by a high-throughput wide-field cell imaging system as previously described35. b, c Neurons were counterstained with MAP2 antibody and the nucleus with DAPI staining. Scale bar = 10 μM. b The left-hand side part of the histogram shows the background of each pS129 antibody in PBS-treated primary neurons, while the right-hand side part of the histogram shows the pS129 level detected by the pS129 antibodies in PFFs-treated primary neurons. c pS129 level in PFF-treated primary neurons was re-evaluated after subtracting the pS129 background level from the PBS-treated neurons. The graphs represent the mean +/− SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001 (ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD post hoc test, PBS vs. PFF-treated neurons). d WB analyses of the insoluble fractions of the PBS- and PFF-treated neurons. Membranes were then counterstained by total aSyn antibodies (SYN-1 or Fl-140 α/β/γ synuclein), and actin was used as a loading control. The red arrows indicate the pS129-aSyn positive bands. The blue arrows indicate the undefined bands. All blots were derived from the same experiment and were processed in parallel.