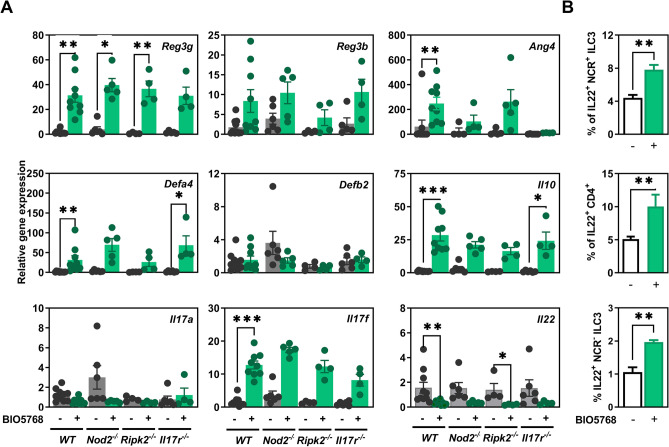
Figure 2.
The anti-microbial abilities of L. acidophilus BIO5768 in vivo is independent of NOD2 and IL-17 signaling. GF female WT (n = 9) or deficient for NOD2 (Nod2−/−; n = 5), RIP2 (Rip2−/−; n = 4), and IL-17 Receptor A (Il17Ra−/; n = 4) were mono-colonized with strain BIO5768 by a single administration (5 × 108 CFU/ mice) and compared to untreated GF WT mice (n = 9). (A) After 30 days mono-association, gene expression by qRT-PCR analysis of Reg3g, Reg3b, Ang4, Defa4, Defb2, Il10, Il17a, Il17f and Il22 in the distal colon and caecum of monocolonized and GF mice. Results are expressed as means ± SEM by comparing the PCR cycle thresholds (Ct) for the gene of interest and for the house keeping gene Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (Gapdh) of mono-colonized animals compared with GF WT mice. (B) Impact of BIO5768 monocolonization on the percentage of IL-22 producing NCR + and NCR− ILC3 and CD4+ T cells within colon and caecum, as determined by flow cytometry. Data represent means values of each group from one gnotobiotic experiment ± SEM. * p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.