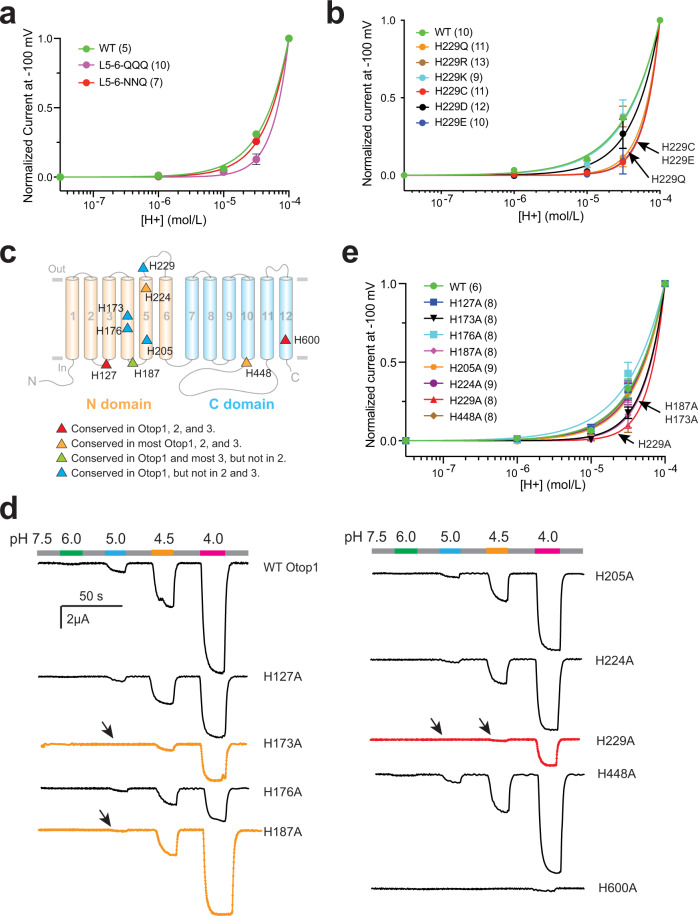
Fig. 3. H229 in L5–6 is a key residue for the proton sensing of the human Otop1 channel.
a, b, e Proton dose–response curves showing the acid sensitivity comparison between the WT and the indicated mutant channels. The currents of every oocyte at other pHs were normalized to the current at pH 4 at −100 mV. The data were fitted by nonlinear regression with variable slope. We were unable to calculate an accurate EC50 of these channels. Since it is not possible to separate the proton sensing and proton conductance in this case, theoretically, we are not able to obtain the saturated proton concentration. c Predicted positions of indicated histidine residues in the topology structure of human Otop1. The residues are colored based on their conservation in Otop proteins as indicated at the bottom. d Gap-free recording shows the currents of indicated histidine mutants at different pHs. The oocytes were held at −60 mV. The currents of H229A, H173A, and H187A, the three mutants that have altered proton sensitivity, are in red or orange. Arrows indicated the missing responses to protons at the indicated pHs.