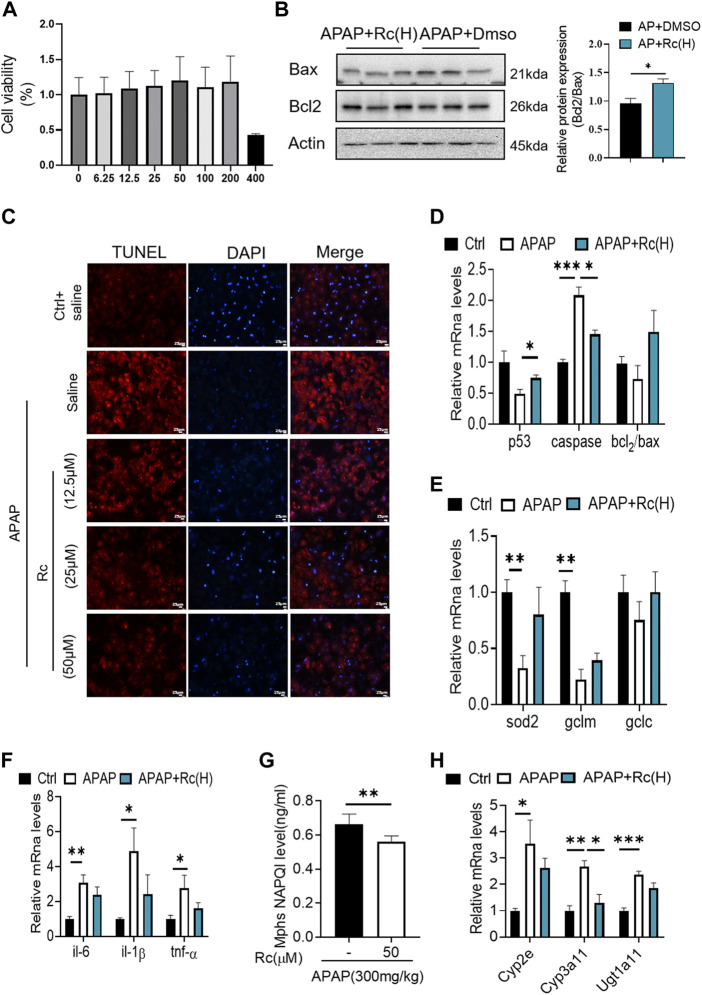
FIGURE 1.
Ginsenoside Rc suppressed APAP-induced hepatocellular damage by reducing oxidative stress, and inflammation in MPHs. (A) CCK8 assay; (B) Ginsenoside Rc treatment inhibits the expression of Bcl2 protein and restrains the expression of bax in MPHs. (C) The TUNEL assay was performed to measure the apoptosis effect in MPHs. (D) Relative expression of mRNA associated with antiapoptosis (P53, Caspase, Bcl2/Bax);(E) Relative expression of mRNA associated with oxidative stress (Sod2,Gclc, Gclm); (F) Relative expressions of mRNA associated with inflammation (Il-6, Il-1β, TNF-α); (G) The ELISA assay showed that Ginsenoside Rc treatment decreased NAPQI levels in MPHs; (H) Relative expression of RNA associated with APAP-metabolizing enzymes (Cyp3a11,Cyp2E,Ugt1a11); Data are means ± SEM; n = 3-6/group.*, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001.