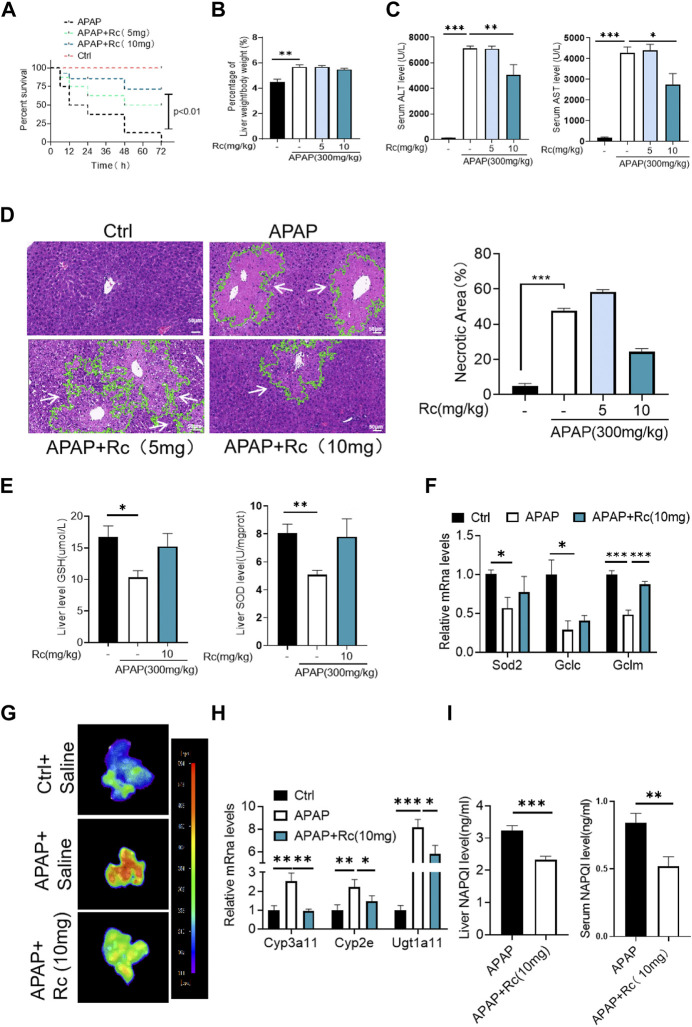
FIGURE 2.
Ginsenoside Rc alleviated hepatic damage in ALI mice by regulating oxidative stress. (A) The survival rate of mice (with/without Ginsenoside Rc treatment) after intraperitoneal injection of APAP for 72 h(B) The ratio of liver weight/body weight; (C) Serum ALT and AST levels; (D) H&E staining of livers (1000×); (E) Hepatic GSH and SOD levels were reduced in APAP-induced mice after Ginsenoside Rc treatment; (F) Expression of mRNA levels of oxidative stress genes (Sod2, Gclc, Gclm); (G) Hepatic ROS levels were decreased in APAP-induced mice after Ginsenoside Rc treatment; (H) Relative expression of mRNA associated with APAP-metabolizing enzymes (Cyp3a11, Cyp2E, Ugt1a11); (I) The ELISA assay showed Ginsenoside Rc treatment decreased NAPQI levels in APAP-administrated mice. Data are means ± SEM; n = 5-8/group. *,p < 0.05, **; p < 0.01, ***; p < 0.001.