Figure 6.
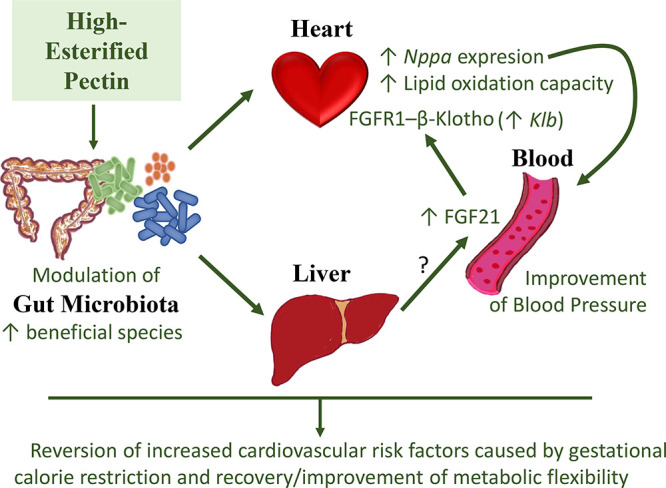
Summary of suggested mechanisms involved in the cardiovascular improvement in gestational calorie-restricted animals, associated with high-esterified pectin (HEP) chronic supplementation. HEP supplementation promotes the modulation of the gut microbiota by favoring the increase in the relative abundance of beneficial species. The changes may indirectly impact critical organs, such as the heart and the liver, modulating gene expression and increasing FGF21 circulating levels. Although the liver is the main productor of FGF21, from our results we cannot distinguish whether the elevated blood levels are caused by increased hepatic secretion or by other tissue/s. FGF21, via its specific receptor FGFR1 and co-receptor β-Klotho, might be partly responsible for the improvements observed in the heart, such as the increase in lipid oxidation capacity and in Nppa expression, which in turn would improve blood pressure. Overall, HEP supplementation reverses the increased cardiovascular risk factors caused by gestational calorie restriction and allows the recovery, or even improvement, of metabolic flexibility.
