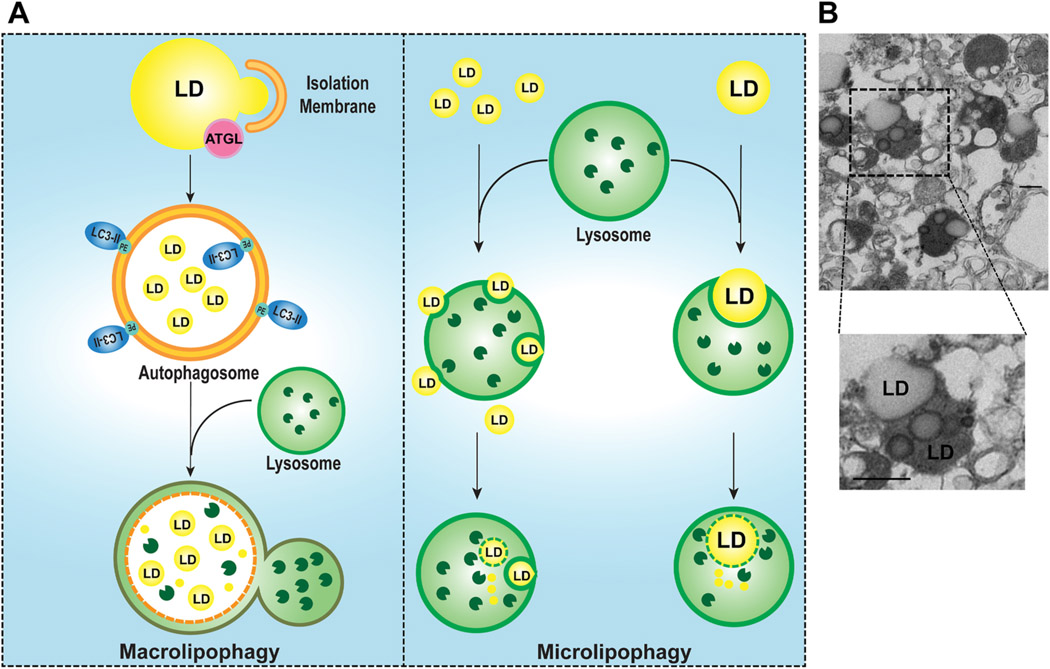
Fig. 3. Macrolipophagy and microlipophagy regulate homeostasis of LDs in the liver.
Two major autophagy pathways are involved in the catabolism of LDs in hepatocytes: Type 1 macrolipophagy and Type 2 microlipophagy (A). In macrolipophagy, the isolation membrane and autophagosome are developed around the LDs and engulfed a portion of the LDs as a result of ATGL-mediated lipolysis in a piecemeal fashion. The autophagosome containing the LD then fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome where the LD is degraded by acidic lipases. In microlipophagy, multiple small LDs or a large LD can be directly taken up by a lysosome via lysosomal membrane invagination, and degraded by lysosomal acidic lipases generating free fatty acids. Whether a receptor protein is required for both lipophagy pathways remains unclear. (B) Representative images of electron microscopy analysis of purified lysosomal fractions from mouse livers that are fasted overnight. Lower panel is enlarged from the boxed area. Arrows: lysosomes with LD.