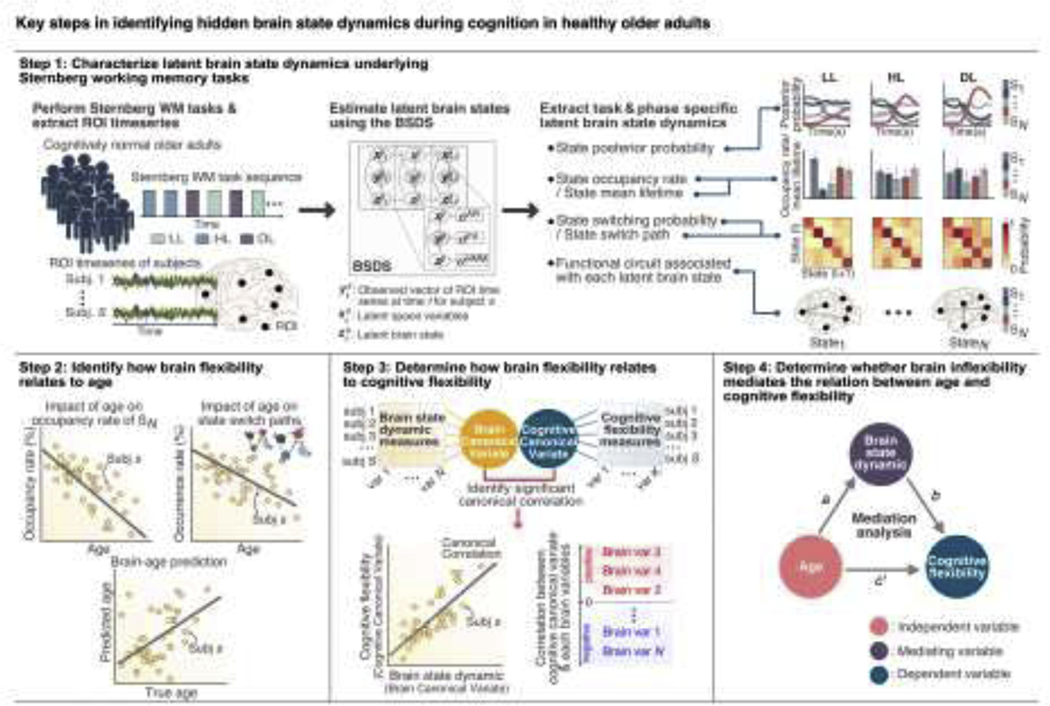
Figure 1. Overall analysis approach for identifying latent brain state dynamics and its relation to age and cognitive flexibility.
Our approach is composed of four analysis steps. In Step 1, we used the Bayesian switching dynamical systems (BSDS) model to determine the evolution of dynamic latent brain states underlying the Sternberg working memory (WM) task. We identified latent brain states (S1 … SN) and characterized their dynamic properties, including (1) posterior probability, (2) occupancy rate and mean lifetime, (3) state switching probability and state switch paths, and (4) functional circuit associated with each latent brain state. In Step 2, we examined how brain flexibility, quantified based on dynamic properties of latent brain states, changes with age in a group of healthy older adults. In Step 3, we determined how brain flexibility relates to cognitive flexibility using canonical correlation analysis with cross-validation and prediction analysis based on brain state properties obtained in Step 1 and neuropsychological measures of cognitive flexibility. In Step 4, we determined whether brain inflexibility mediates the relation between age and cognitive flexibility in healthy older adults.