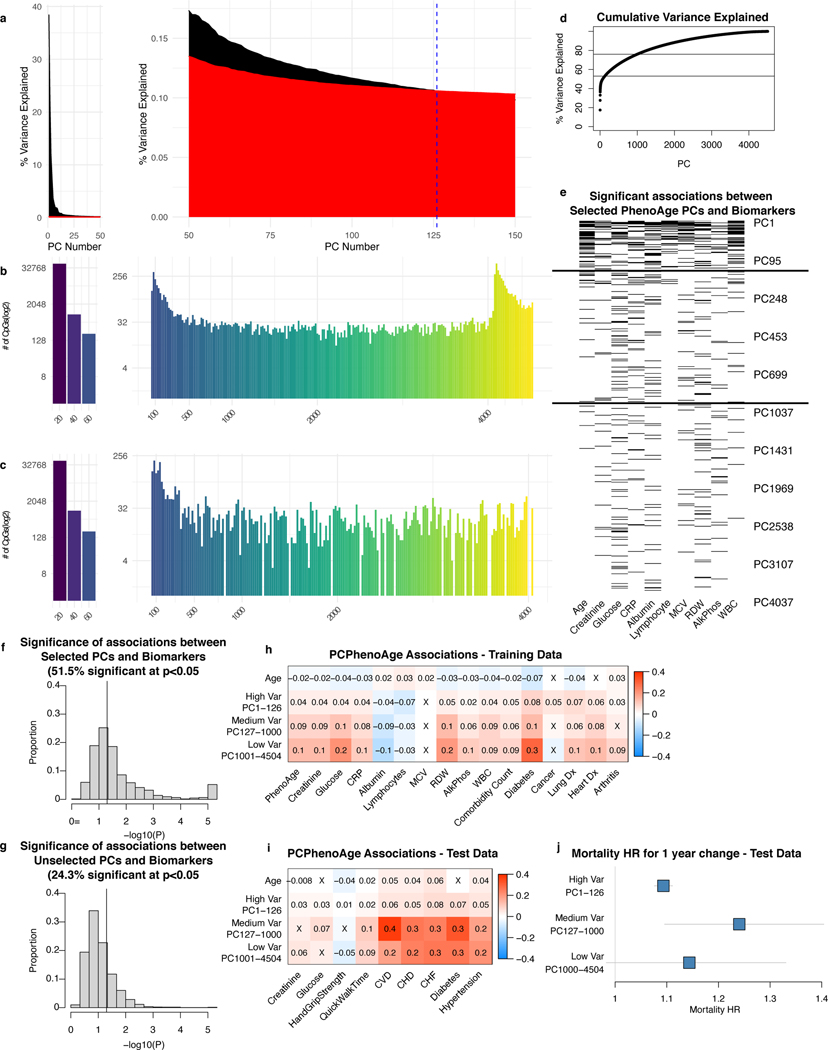
Extended Data Fig. 7. Low-variance PCs capture aging heterogeneity in physiological systems.
a, Scree plots showing variance explained by PC for PCPhenoAge in training data (black) compared to variance explained for a randomized matrix of the same size as PCPhenoAge training data (red), for the top 150 PCs (split into two graphs for visualization purposes). b-c, Number of new driver CpGs introduced by each PC for all PCs (b) and PCs included in the model (c). d, Cumulative variance plot for PCPhenoAge. e, Plot showing significant univariate linear associations between PhenoAge components and PCPhenoAge PCs, with PCs ordered from highest to lowest variance explained. These were not adjusted for multiple testing as the PCs are meant to be combined by elastic net regression. For d and e, the horizontal lines delineate the selected cutoffs for high-, medium-, and low-variance PCs. f-g, Histograms of the association significance for selected PCPhenoAge PCs (f) and unselected PCs (g), with values reported as -log10(p-value), with significance determined by two-sided t-test, not adjusted for multiple testing. Vertical lines denote p = 0.05. For each PC, we selected the most significant p-value out of the 10 PhenoAge components. h-i, PCPhenoAge was divided into components corresponding to the signal from high-, medium-, and low-variance PCs in both HRS training data (h) and FHS test data (i). Multivariate associations between biomarkers and disease status are shown. Biomarkers were standardized (Z-scores) and modeled using linear regression. Disease status was binary and modeled with logistic regression. PCPhenoAge components were in units of 1 year. For example, a 1-year increase in PCPhenoAge due to medium-variance PCs was associated with a 0.1 SD increase in creatinine in training data and a 0.06 SD increase in test data. Non-significant correlations are denoted by “X”. j, Mortality hazard ratios for a 1-year change in PCPhenoAge components from high-, medium-, and low-variance PCs are shown (n = 3935 with 319 deaths). Data are presented as HR estimate with 95% confidence interval.