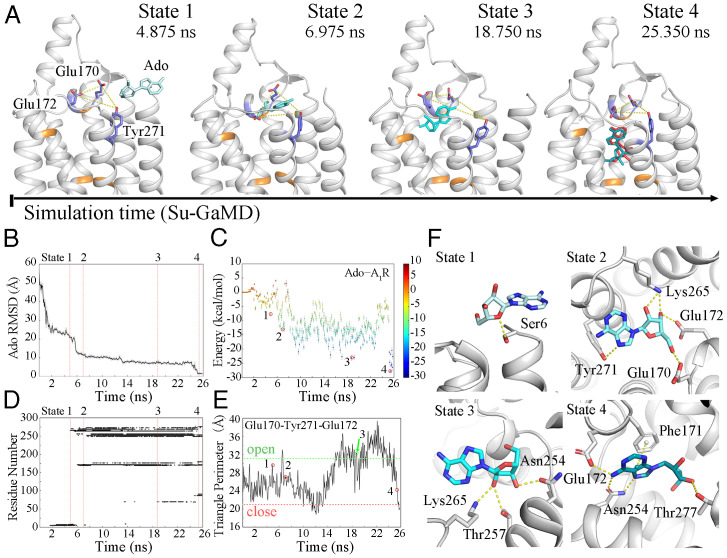
Fig. 2.
(A) The Ado–A1R recognition process. A1R is shown in silver; residues Thr913.36, Phe171ECL2, Leu2506.51, Asn2546.55, Thr2777.42, and His2787.43 are shown in orange; and Glu170ECL2, Glu172ECL2, and Tyr2717.36 are shown as blue sticks. Ado is shown as a cyan stick, and the pose of Ado in the 6D9H structure is colored red in state 4. Time-dependent (B) Ado rmsd, (C) binding free energy landscape for Ado–A1R, (D) Ado–A1R contact residues, and (E) the triangle perimeters of the Glu170ECL2–Tyr2717.36–Glu172ECL2 vestibular lid during the recognition process (the triangle perimeters of the open and closed states are depicted in green and red dashed lines). (F) The four metastable intermediate states in the Ado–A1R recognition pathway.