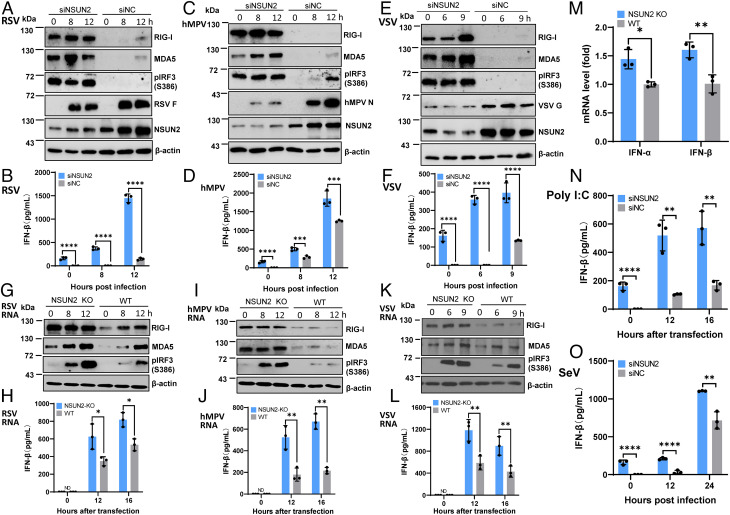
Fig. 4.
NSUN2 depletion leads to the activation of a higher type I IFN signaling pathway. (A–F) NSUN2 depletion induces a higher type I IFN after virus infection. A549 cells were transfected with siNSUN2 or siNC, and were infected with rgRSV (A and B), hMPV (C and D), or rVSV-GFP (E and F) at an MOI of 1.0, 5.0, and 1.0, respectively. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analyses (A, C, and E). IFN-β in cell culture supernatants was detected by ELISA (B, D, and F). (G–L) NSUN2 KO induces a higher type I IFN after transfection with viral RNA. NSUN2-KO or control A549 cells were transfected with virion RNAs (2 × 106 copies/well) of rgRSV (G and H), hMPV (I and J), or rVSV-GFP (K and L). ND indicates the value was below the detection limit (50 pg/mL). (M) Quantification of IFN mRNA by RT-qPCR. Total RNA was extracted from NSUN2-KO or control sgRNA-treated A549 cells. IFN-α and IFN-β mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR. β-actin was used for internal control. (N) NSUN2 KO induces a higher type I IFN after transfection with poly(I:C). Cells were transfected with 0.5 µg/well of poly(I:C). (O) NSUN2 KO induces a higher type I IFN after infection with rSeV-GFP. An MOI of 1.0 was used for infection. Data were analyzed using a Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).