Figure 2.
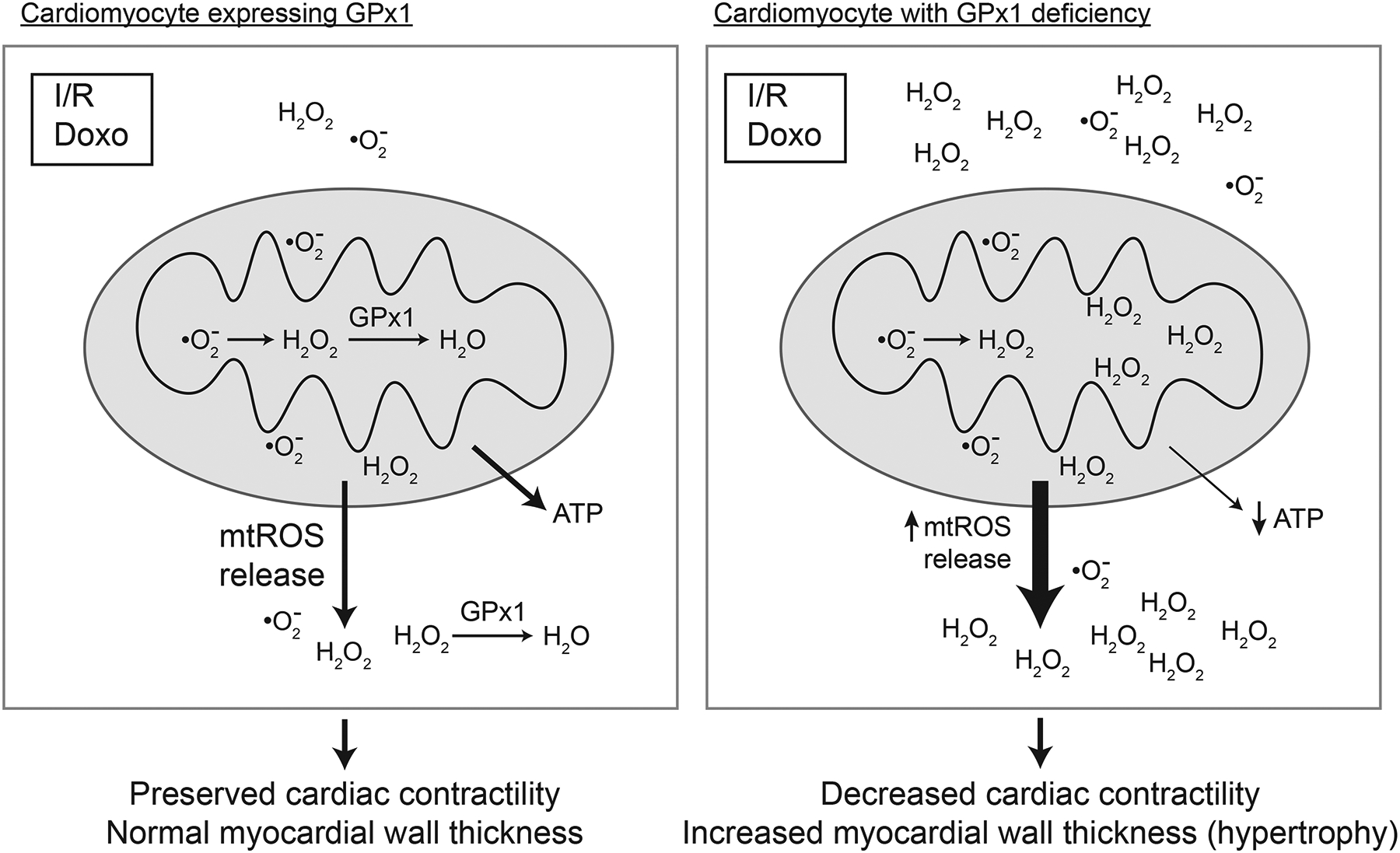
Dysfunction of cardiac mitochondria is augmented by GPx1 deficiency. Stressors such as ischemia reperfusion (I/R) and exposure to cardiotoxins, such as doxorubicin (Doxo), are associated with increased production of superoxide and/or hydrogen peroxide. In the absence of GPx1, ROS accumulates and promotes mitochondrial dysfunction. Oxidant mediated damage to mitochondrial lipids, proteins, and DNA enhances the accumulation of oxidants, in part, by uncoupling mitochondrial oxygen consumption and ATP production to produce more superoxide and increase mitochondrial release of ROS (mostly as hydrogen peroxide but superoxide may also be released). Mitochondrial dysfunction correlates with cardiac dysfunction including decreased cardiac contractility and hypertrophy, changes that are augmented with GPx1 deficiency. Note that in the context of doxorubicin exposure, transgenic mice overexpressing GPX1 showed less cardiac and mitochondrial dysfunction than wildtype hearts expressing normal levels of GPx1.
