Figure 4.
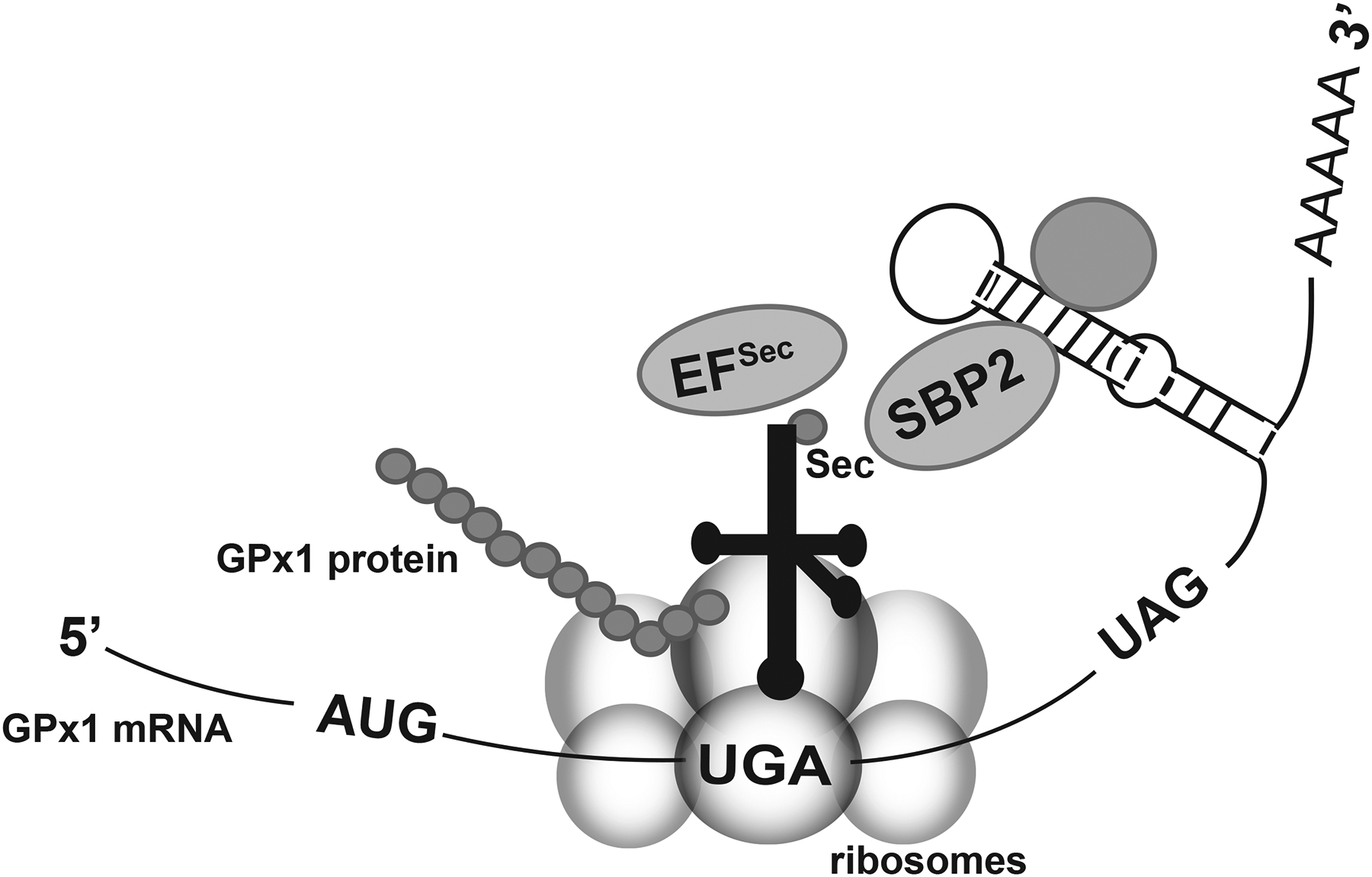
Incorporation of selenocysteine at a UGA codon during translation. Selenocysteine incorporation involves many unique cofactors to allow for the insertion of selenocysteine (Sec) at a UGA codon instead of terminating translation. The selenocysteine tRNA associates with the elongation factor for selenocysteine incorporation (EFSec) and the SBP2 protein. SBP2 also binds to the stem-loop structure (SECIS element) in the 3’ untranslated region of selenoprotein transcripts. Additional proteins may bind to the SECIS element (represented by the unlabeled shaded circle). Note that the codon that terminates GPx1 translation is UAG. (Modified from Lubos et al [2]).
