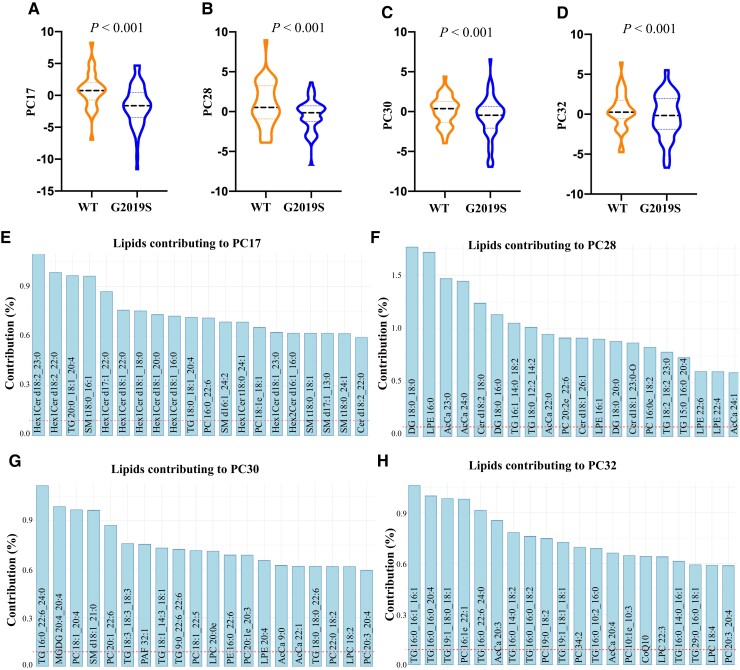
Figure 2.
Serum lipid profiles discriminate LRRK2 G2019S carriers from non-LRRK2 G2019S carriers in a multi-ethnic cohort. To determine which lipids may contribute to the discrimination of LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers from non-LRRK2 G2019S carriers, linear discriminant analysis (LDA) was performed to identify the principal components that significantly differed between these two groups. The LRRK2 mutation group consisted of both asymptomatic carriers and manifesting Parkinson’s disease patients, while the non-LRRK2 mutation group consisted of control and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease patients. LRRK2 mutation carriers could be significantly discriminated from non-LRRK2 mutation carriers. (A–E) Multivariate ANOVA covarying for age and sex identified four principal components, (B) PC17, (C) PC28, (D) PC30 and (E) PC32, were significantly different between LRRK2 and non-LRRK2 mutation groups. (F–H) The top 20 lipid species that contributed to the four principal components discriminating LRRK2 and non-LRRK2 mutation groups. The dashed red line represents the expected value if the contribution of lipids were uniform. n = 221. WT = wild-type.