Figure 1.
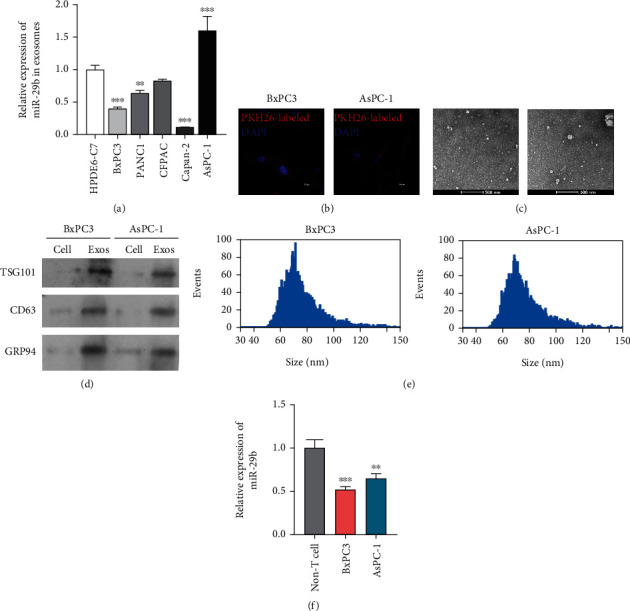
Identification of exosomal miR-29b originating from PC cells. (a) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-29b in exosomes extracted from HPDE6-C7, BxPC3, PANC1, Capan-2, and AsPC-1 cells. ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. HPDE6-C7. (b) After coincubation with PKH26-labled exosomes, HUVECs were counterstained with a nuclear marker (DAPI) and viewed under a confocal microscope (200x). (c) TEM image of exosomes isolated from BxPC3 and AsPC-1 cells (8000x). (d) Western blot analysis of TSG101 and CD63 protein expression in exosomes derived from BxPC3 and AsPC-1 cells. Protein samples from BxPC3 and AsPC-1 cells served as negative controls. (e) Particle size of exosomes was analyzed. (f) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-29b expression in BxPC3 cells, AsPC-1 cells, and non-T cells. ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. non-T cells. Experiments were repeated for three times and presented as mean ± SD.
