Figure 3.
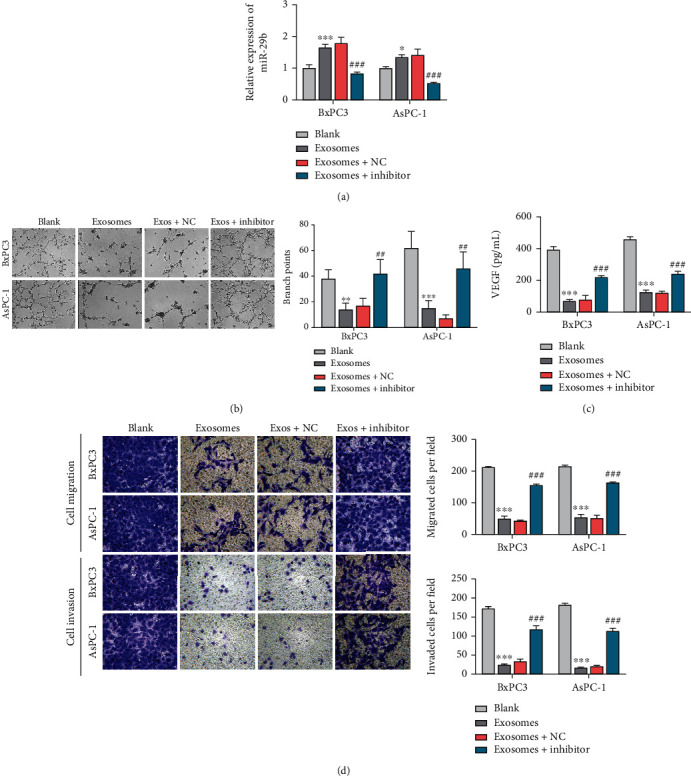
Exosomal miR-29b from PC cells enhanced HUVEC migration and tube formation. (a) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-29b expression in recipient HUVECs incubated with exosomes secreted from BxPC3 and AsPC-1 cells transfected with miR-29 mimics and also in recipient HUVECs treated with the miR-29b inhibitor or inhibitor NC. The parental HUVECs served as blank control cells. (b) Tumor formation assays were performed on HUVECs treated with exosomes, exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor, and exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor NC (100x). The parental HUVECs served as blank control cells. (c) ELISA detection of VEGF levels in HUVECs treated with exosomes, exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor, and exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor NC. The parental HUVECs served as blank control cells. (d) Transwell migration assays for determining the migration of HUVECs treated with exosomes, exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor, and exosomes+miR-29 inhibitor NC. The parental HUVECs served as blank control cells (200x). ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. blank; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 vs. exosomes+NC. Experiments were repeated for three times and presented as mean ± SD.
