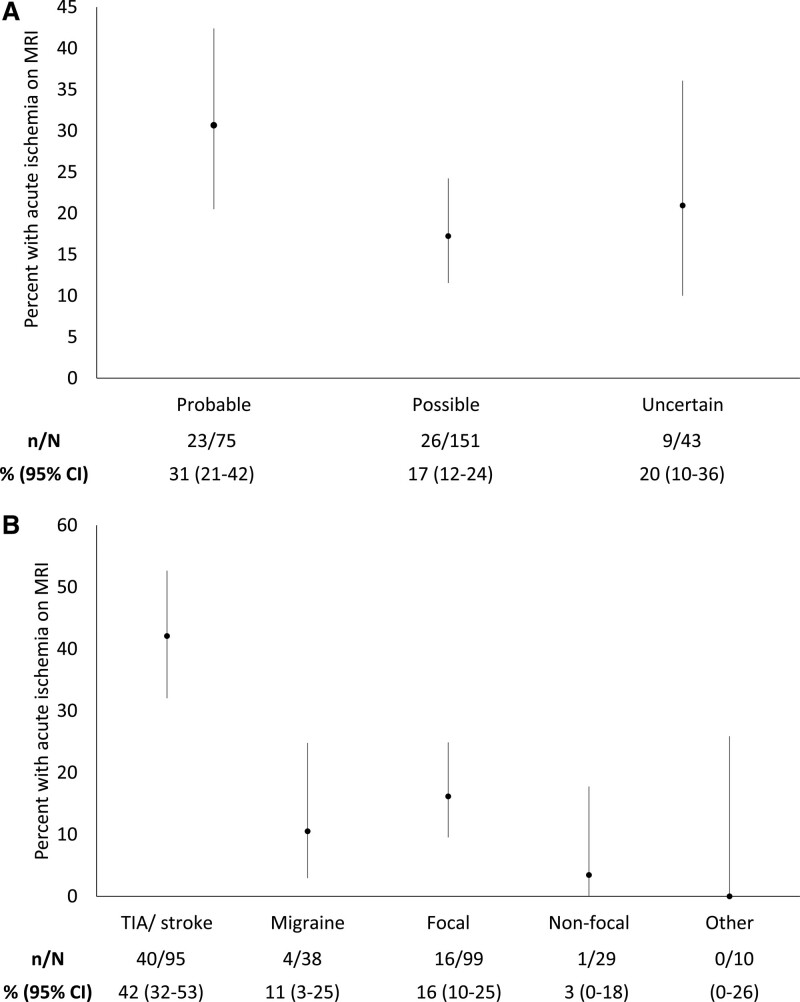
Figure 1.
Percentage of participants with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence of acute ischemia. A, With a prospectively provided clinical diagnosis of probable, possible, or uncertain stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA; χ2 P=0.07). B, With a retrospective diagnosis of TIA or stroke by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) definition; migraine; focal non-NINDS attacks; nonfocal symptoms; or other diagnosis.