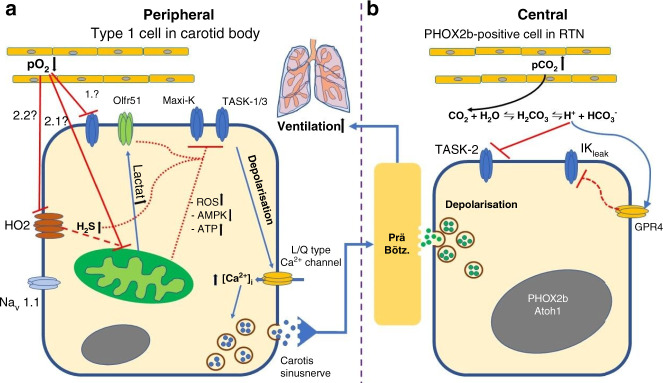
Fig. 1. Cell models of peripheral and central chemoreception.
a Proposed mechanism of oxygen-sensing in the carotid body. An inhibition of potassium channels (TASK-1/3, maxi-K+) in type I cells induces a depolarization of the cell membrane with activation voltage-sensitive Ca2+ influx. Two main different theories exist, how the inhibition of membrane K+ channels takes place: (1.) Hypoxia induces direct inhibition of the K+ channels or (2.1/2.2) a rise of metabolic factors, like ROS, in the mitochondria inhibits the K+ channels. pO2 partial pressure oxygen; HO2 heme-oxygenase 2; H2S hydrogen sulfide; Nav1.1 voltage-gated sodium channel type I; ROS reactive oxygen species; L/Q-type Ca2+ channel voltage-gated calcium channel; TASK-1 + 3 Twik (Tandem of P-domains in a Weakly Inward rectifying K+ channel)-related acid-sensitive potassium channels; Maxi-K+ large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel; Olfr51 Olfactory receptor family 51, Glu glutamate. b The currently accepted model of CO2 measurement in the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) of the brainstem. Increase of partial CO2 pressure (pCO2) and thereby acidification of the cerebroid fluid directly inhibits TASK-2 and directly activates GPR4. The inhibition of TASK-2 and other K+ channels (IKleak) by GPR4 depolarize cell membrane of the PHOX2B positive neurons and induces thereby neurosecretion. ATP adenosine-tri-phosphate; pCO2 partial pressure of carbon dioxide; TASK-2 Twik (Tandem of P-domains in a Weakly Inward rectifying K+ channel)-related acid-sensitive potassium channels; GPR4 G-protein-coupled receptor 4; IKleak leak potassium channels; CPG central pattern generator; PHOX2B paired-like homeobox 2B; ATOH1 atonal homolog 1.