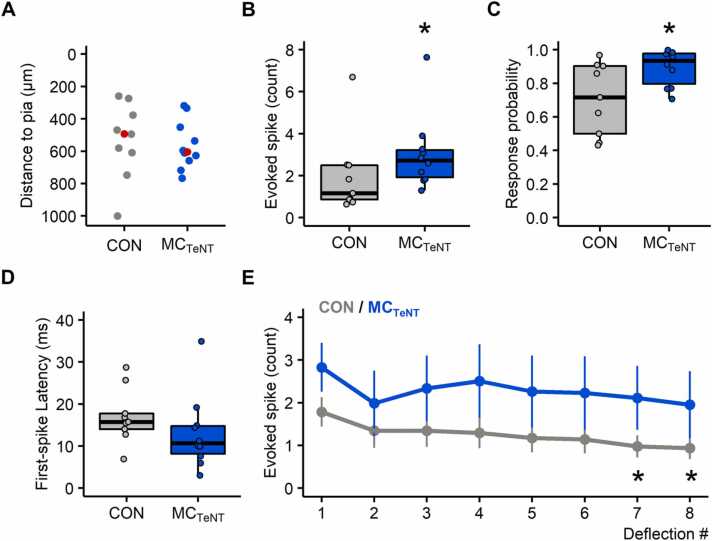
Fig. 2.
Overall effect of reducing MC activity on whisker-evoked wS1 spiking, response probability, first-spike latency, and response adaptation to repetitive deflection. (A) Relative depth distribution to pia of the recorded wS1 neurons (CON: n = 9; MCTeNT: n = 10), red markers indicating the median recording depth. (B-D) Boxplots showing the grand-average effect (collapsed across the six different whisker deflection paradigms) of reducing MC activity on the number of whisker-evoked spikes, response probability and first-spike latency (over a 100 ms response window) (CON: n = 9; MCTeNT: n = 10). (E) Average number of evoked spikes along 8 repetitive whisker deflection delivered at 8 Hz (CON: n = 7; MCTeNT: n = 7), data shown as Mean ± SEM. (*) Indicates significant differences in controls between 1st/7th and 1st/8th deflection pairs. (A-D) Wilcoxon rank sum test. (E) Friedman test followed by Conover’s all-pairs posthoc test.