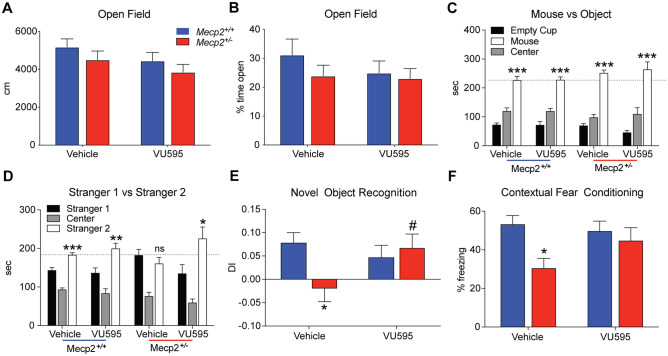
Fig. 2.
M1 potentiation with VU0467595 (VU595) improves social and cognitive phenotypes in the Mecp2+/- model of Rett syndrome. N = 13 Mecp2+/+/treatment group, N = 11 Mecp2+/-/treatment group. A–B Open field. Neither genotype nor VU595 administration (10 mg/kg, ip) had an impact on spontaneous locomotion (A) and anxiety phenotypes (B) relative to vehicle Mecp2+/+ control mice. C–D Three-chamber social interaction assay. No genotype or compound effect was observed in the sociability phase of the assay (C), as all mice demonstrated a preference for the stranger 1 mouse over the empty cup. When exposed to a familiar (stranger 1) and a novel (stranger 2) mouse, Mecp2+/+ mice showed a preference for social novelty, independent of treatment. Conversely, vehicle-treated Mecp2+/- mice did not distinguish between stranger 1 or stranger 2, and VU595 treatment restored preference for the novel mouse. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. E Novel object recognition. DI, discrimination index. Vehicle-treated Mecp2+/- mice did not show a preference for the novel object over a familiar object, indicative of a deficit in spatial memory. VU595 administration significantly improved this phenotype in Mecp2+/- mice. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. F Contextual fear conditioning. Vehicle-treated Mecp2+/- mice presented with significantly decreased freezing when re-exposed to an aversive environment, suggesting an impairment in associative memory. Treatment with VU595 before the training phase of this assay normalized freezing in Mecp2+/- mice to levels comparable to Mecp2+/+ controls. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. Ns, not significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p, 0.001. #p < 0.05 within genotype comparison