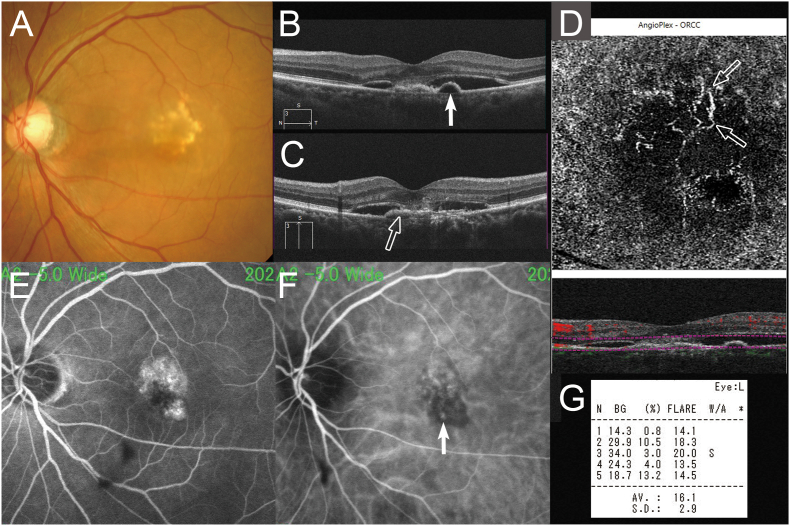
Fig. 1.
A 72-year-old woman with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy treated by switching aflibercept to brolucizumab. At baseline, the best-corrected visual acuity (VA) was 0.10 logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution VA (Snellen equivalent: 20/100). (A) A color fundus photograph shows serous retinal detachment (SRD) and lipids. Horizontal (B) optical coherence tomography (OCT) shows SRD and protrusion of the highly reflective retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) line (arrow) corresponding to the polypoidal lesions (arrow) on early-phase indocyanine green (ICG) angiography (F). (C) Vertical OCT shows SRD and the flat elevation of the RPE layer as two separate, highly reflective lines (double-layer sign) (arrow) corresponding to occult choroidal neovascularization on fluorescein angiography (E), which is depicted by OCT angiography as a hyperflow lesion (D). The laser flare-cell photometer shows a value of 16.1 photon count/ms. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)