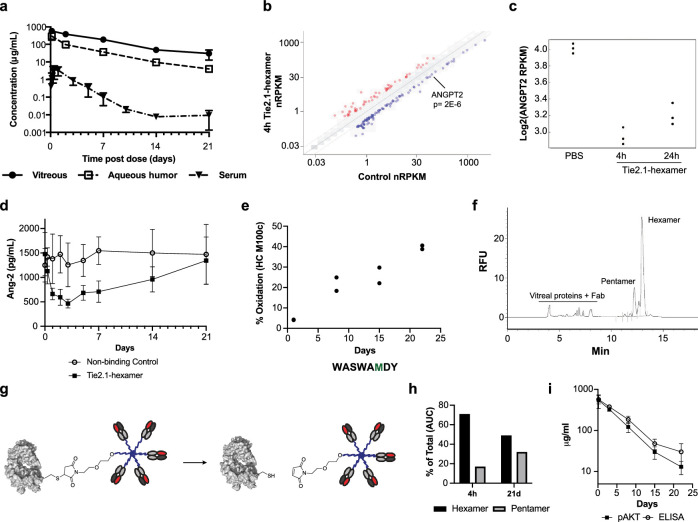
Figure 4.
In vivo exposure, activity, and stability of Tie2.1-hexamer. (a) Pharmacokinetic profiles of Tie2.1-hexamer following 2-mg/eye bilateral intravitreal injection into male cynomolgus monkeys. (b) RNA-sequencing analysis of gene expression levels in primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells treated with 10 µg/mL of Tie2.1-hexamer or PBS for 4 hours compared to control. (c) Ang-2 RNA-sequencing expression levels in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells treated with PBS or 10 µg/mL of Tie2.1-hexamer for 4 hours or 24 hours. (d) ELISA analysis of Ang-2 levels in monkey plasma following treatment with Tie2.1-hexamer or a non-binding control. (e) LC-MS/MS analysis of Tie2.1-hexamer isolated from monkey vitreous 4 hours to 21 days following administration. Sequence of the relevant peptide is shown with the oxidized residue in green. (f) CE–SDS–LIF electropherogram of monkey vitreous isolated 4 hours following intravitreal injection of Tie2.1-hexamer. (g) Schematic showing retro-Michael decomposition of Tie2.1-hexamer into a Tie2.1-pentamer and Fab. (h) CE–SDS–LIF quantitation of Tie2.1-hexamer and Tie2.1-pentamer in monkey vitreous isolated 4 hours and 21 days following intravitreal administration of Tie2.1-hexamer. (i) Concentrations of Tie2.1-hexamer in monkey vitreous determined by pAKT activation versus ELISA signal. Data shown in (a), (d), and (i) are mean ± SD. Error bars are not included if they are less than the size of the marker.