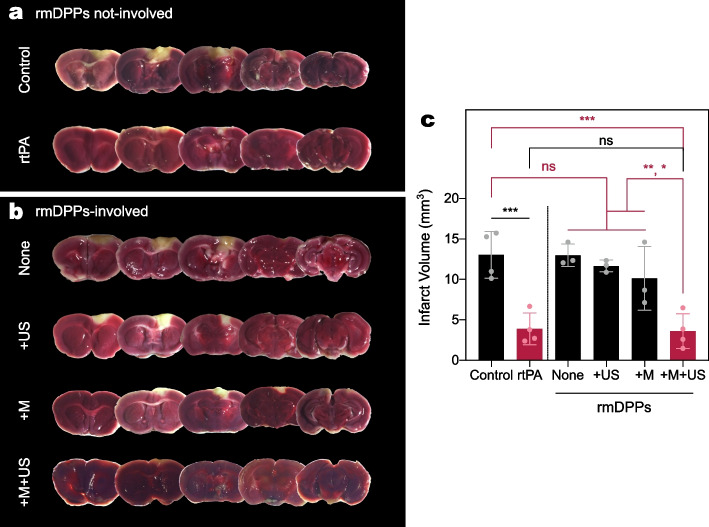
Fig. 7.
Evaluation of the in vivo magneto-sonothrombolytic potential of rmDPPs. (a-b) Typical TTC-stained brain slices after the respective treatments. (c) Quantification of the infarct using the TTC-stained brain slices ( for the control, rtPA, and +M+US groups; for None, +US, and +M groups), showing that only successful recanalization in cerebral vessels was achieved through simultaneous magnetic and acoustic stimuli with rmDPPs. Group information: rmDPPs without any external stimulus for None group; rmDPPs with sole magnetic attraction for +M group; rmDPPs with sole acoustic stimulus for +US group; rmDPPs with the simultaneous stimuli for +M+US group