FIGURE 1.
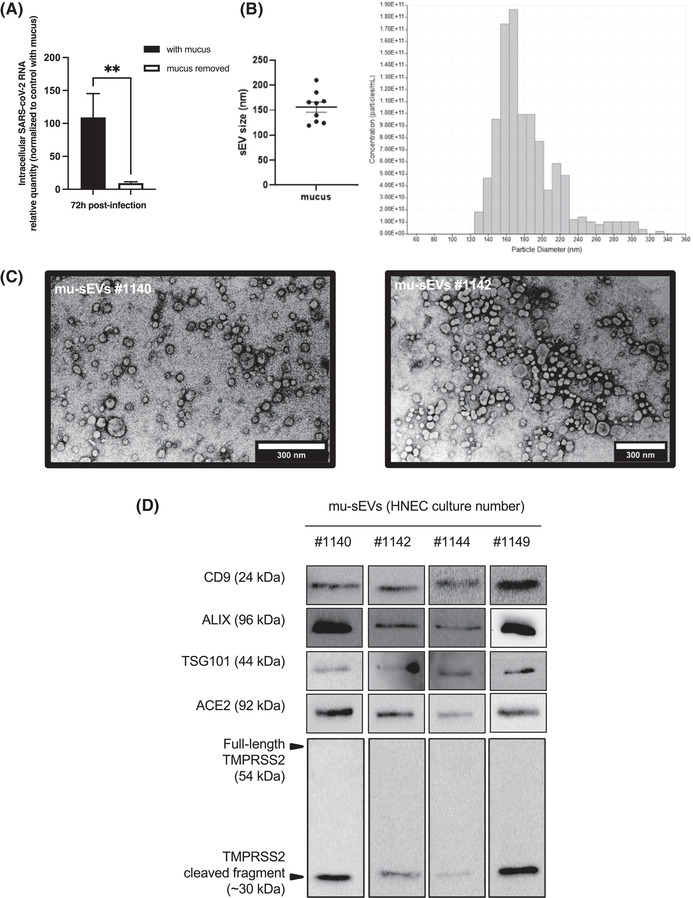
Effect of nasal mucus removal on SARS‐CoV‐2 infection of HNECs and characterization of mu‐sEVs. (A) Intracellular RNA was extracted 72 h post‐infection from HNECs isolated from three different patients, infected for 4 h with SARS‐CoV‐2 (20 μl of viral inoculum, ∼2.04 × 104 TCID50/ml) at the apical pole, in the presence or after removal of cell‐produced mucus. SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA was quantified by RT‐qPCR and the results were normalized to 18S rRNA, then to control with mucus ( = 100%). They are expressed as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01. (B) sEVs isolated from ∼5 ml of mucus (mu‐sEVs) produced by HNECs from nine different patients analysed by tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS). Left panel: TRPS results from nine mu‐sEVs indicating a mean peak particle size of 155.9 ± 30.83 nm in diameter. Right panel: TRPS results obtained from one representative mucus. (C) mu‐sEVs isolated from two patients adsorbed on copper grid, dried at room temperature, stained with uranyl acetate 1% and imaged by transmission electron microscopy. Scale bar: 300 nm. (D) Western blot analysis of CD9, ALIX, TSG101, ACE2 and full‐length and cleaved TMPRSS2 proteins using the amount of 109 mu‐sEVs isolated from four different patients
