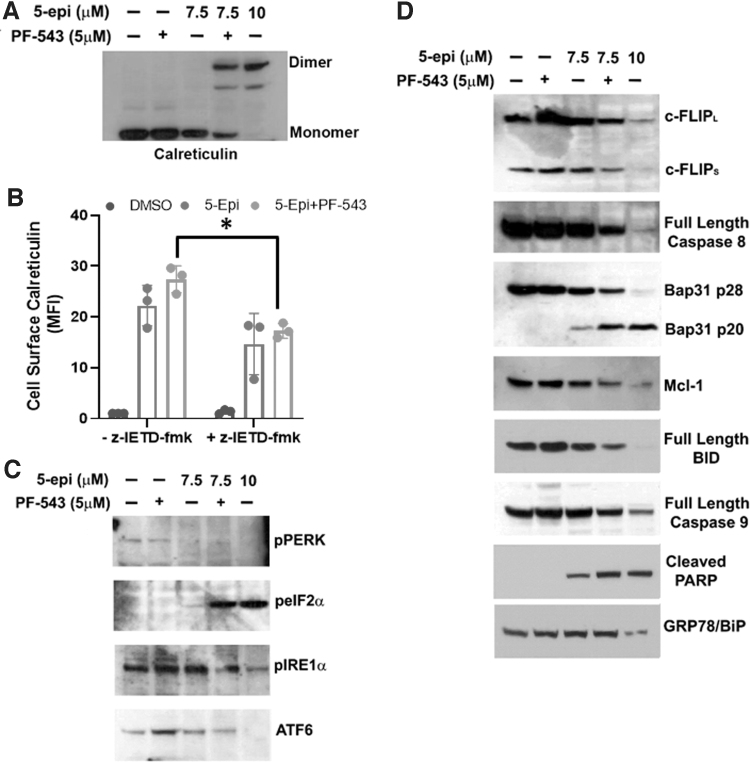
FIG. 3.
5-epi attenuates ER stress/UPR and induces ICD signaling pathways in a Casp8-dependent manner in CRC cells. (A) The oligomeric state of CRT was examined by nonreducing SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of DLD-1 whole cell lysates treated as indicated for 48 h. Representative blot of results from three independent experiments. (B) 5-epi-induced ectoCRT exposure is attenuated by inhibition of Casp8 activity (z-IETD-fmk, 10 μM) in DLD-1 cells, after 48 h of treatment, as determined by flow cytometric analysis using PE conjugated anti-CRT antibodies. Results are presented as average MFI normalized to vehicle (DMSO)-only controls. (*p=0.0206). (C) DLD-1 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of 5-epi and PF-543 for 48 h. 5-epi at high concentrations (10 μM) and in combination with PF-543 (5 μM) at lower concentration (7.5 μM) reduces activity/expression of the UPR markers PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6 as determined by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Phosphorylation of eIF2α at Ser51 is increased by 5-epi alone (10 μM) or in combination with PF-543 as indicated by Western blot analysis using phosphoselective antibodies. Representative blots of results from three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analysis of the signaling pathway associated with ICD in DLD-1 cells treated with 5-epi and PF-543 at the indicated concentrations, for 48 h, using the indicated antibodies. GRP78/Bip serves as a loading control. Representative blots of results from three independent experiments. Casp8, caspase 8; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ICD, immunogenic cell death; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; UPR, unfolded protein response.