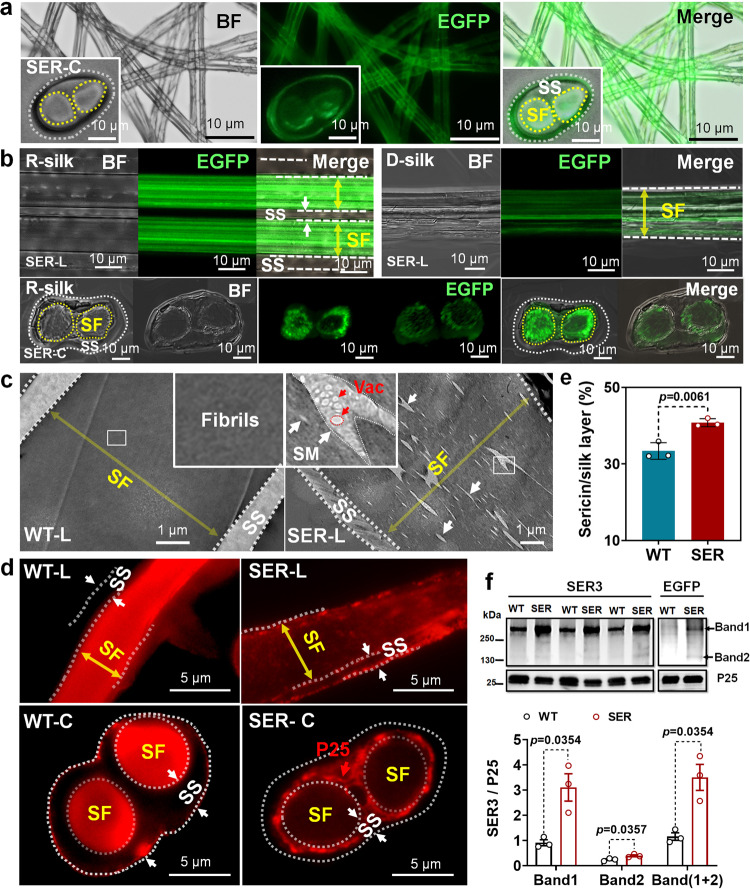
Fig. 2. Distribution of SER3 recombinant protein synthesized by the PSG in cocoon silk and its effect on fiber structure.
Images of silk fibers observed under a fluorescence microscope and b laser confocal microscope. EGFP fluorescence localization of SER3 recombinant protein synthesized by the PSG in silk fiber. c Transmission electron micrograph of a longitudinal silk fiber section. SER3 protein synthesized by the PSG is dispersed in the fibrils of the silk fiber. d Immunofluorescence localization of P25 protein in silk fiber. in Fig. 2a to Fig. 2d: WT-L and SER-L, longitudinal section of silk fiber; WT-C and SER-C, cross-section of silk fiber; R-silk, raw silk; D-silk, degummed silk. SF, fibroin layer of silk. SS, sericin layer of silk. SM, sericin protein microsomes in the silk fibroin fibrils. Vac, vacuoles. e Sericin content of cocoon silk was determined by a classical degumming method. Data were presented as mean ± SEM, and the unpaired t-test analysis was used for the comparison between the two groups. n = 3 cocoons. f The content of SER3 protein in cocoon silk is determined by western blotting; P25 is an internal reference. n = 3. EGFP localization showed that the recombinant SER3 protein had haploid and dimer 2 types, and dimer was the main type. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. Image data are representative of three independent experiments unless otherwise stated.