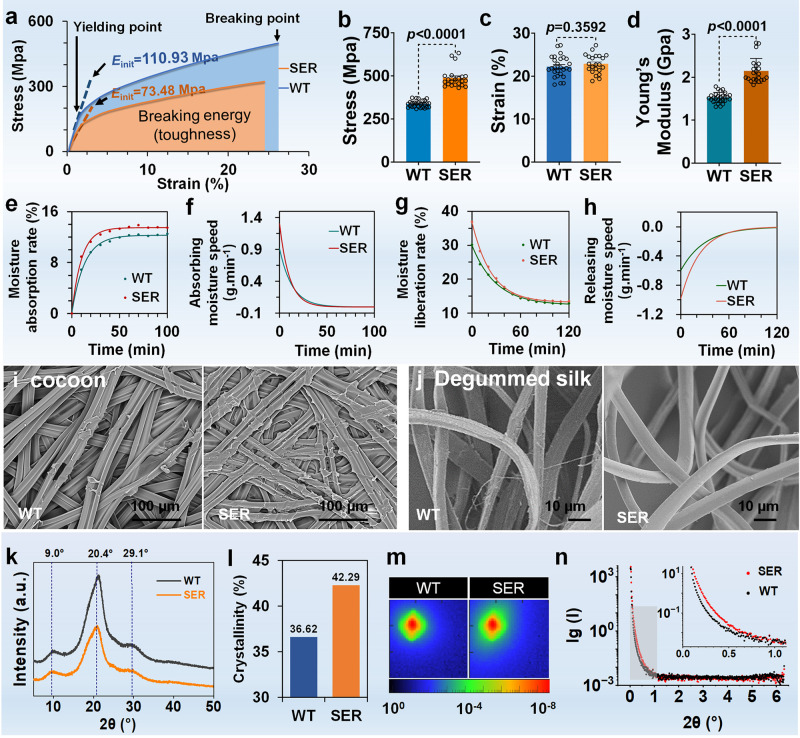
Fig. 3. The SER3 protein secreted by the PSG improves the physical properties of silk fibers.
a–d Fiber mechanical properties. Reeling 20/22 dtex raw silk from cocoons (20 cocoons of WT or SER: one sample was taken every 3–4 meters between 100–200 m to determine the mechanical properties. n = 22 cocoons in SER and n = 27 cocoons in WT. a Stress and strain curve. b Stress level. c Modulus of elasticity. d Young’s modulus. Data were presented as mean ± SEM, and the unpaired t test analysis was used in (b-d). e–h Moisture absorption and desorption performance. The monofilament extracted from cocoons was boiled with 0.2% sodium carbonate for 30 min to remove the outer sericin protein and obtain textile fibroin fiber. e Moisture absorption rate (constant temperature and humidity conditions: 20 °C ± 2 °C, R.H. 65% ± 3%). f Moisture absorption speed. The fitted curve equations of WT and SER fibroin fiber samples are v = 12.276–12.163e-0.0756t, R2 = 0.9966; v = 13.470–13.370e-0.0980t, R2 = 0.9954. t, time. g Moisture liberation rate (constant temperature and humidity conditions: 20 °C ± 2 °C, R.H. 100%). h Moisture release speed. The fitted curve equations of WT and SER fibroin fiber samples are v = 12.353 + 17.619e- 0.03381t, R2 = 0.9977; v = 13.184 + 23.552e-0.04187t, R2 = 0.9990. t, time. i, j Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) characterization of cocoon (i) and fibroin fiber (j). Image data are representative of three independent experiments unless otherwise stated. k XRD pattern of cocoon silk. l Crystallinity of cocoon silk. m SAXS diffractogram of cocoon silk. n SAXS diffraction data. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. n = 3 samples in (e–n).