Figure 2: Chemogenetic inhibition of ACx interneurons reverses frequency-discrimination hyperacuity in CD+/− mice.
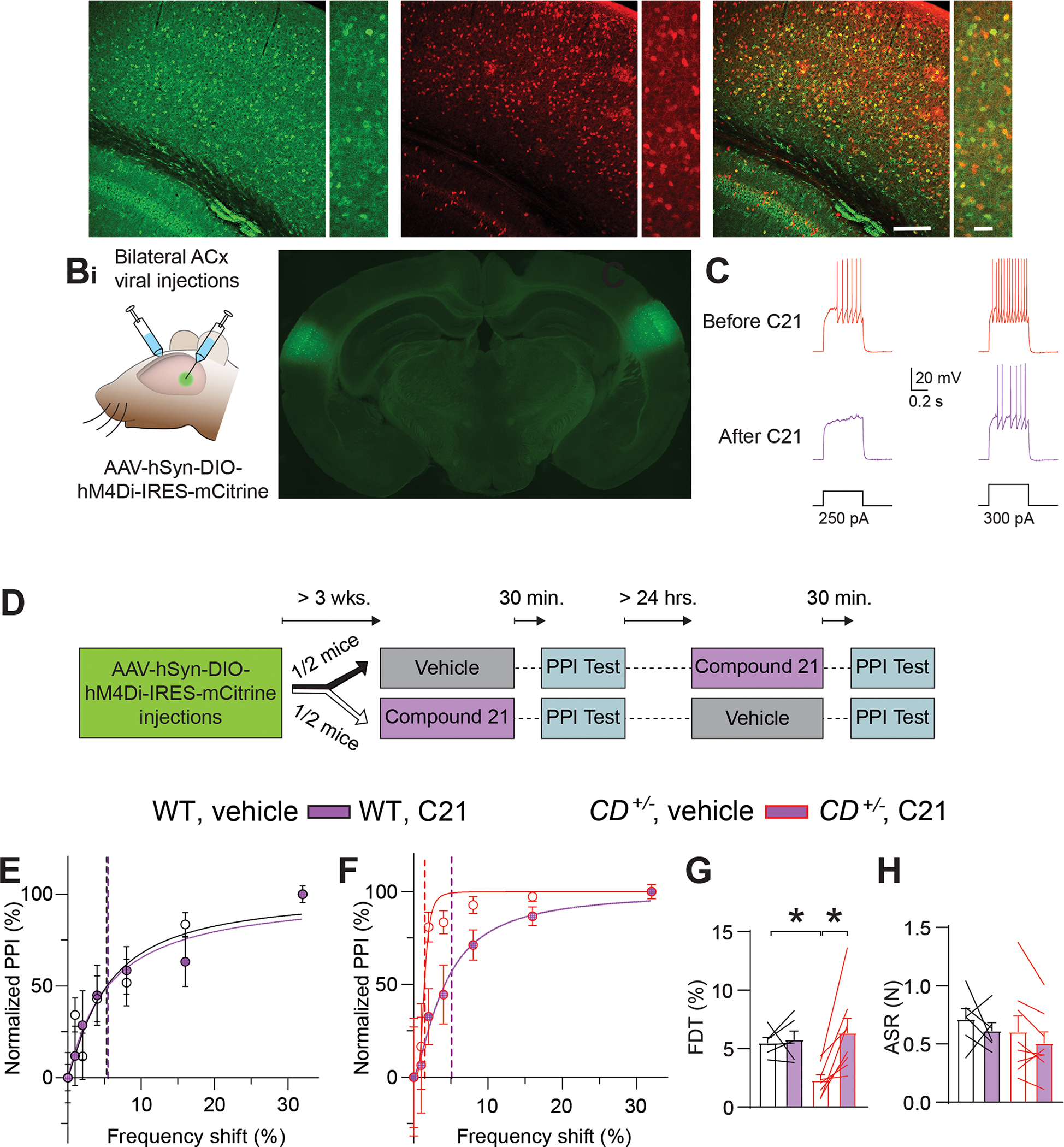
A. Images of GABA+ cells in the ACx (Ai), Gad2Cre–dependent tdTomato fluorescence (Aii), or both (Aiii). Lower (left) and higher (right) magnification images are shown for each.
B. Chemogenetic experiments. Bi. Scheme showing bilateral stereotactic injection of virus into the ACx. Bii. Coronal brain section with targeted bilateral injection of rAAVs encoding GFP into the ACx.
C. Compound 21 (C21) inhibits hM4Di+ interneurons. Responses to two intensities of depolarizing current injection in an hM4Di-expressing FS interneuron before (top) and after (bottom) C21 application in CD+/− mice.
D. Experimental timeline for behavioral testing of the effect of chemogenetic inhibition of interneurons.
E, F. Normalized PPI magnitude in individual WT (E) and CD+/− (F) mice, as a function of frequency difference between background and pre-pulse tones after intraperitoneal injection of vehicle or C21. Symbols and error bars are mean ± SEM of 10 repeated measurements in the same animal. Solid lines are linear-regression fits; dotted lines are frequency-discrimination thresholds (FDTs).
G. The FDT is reversed in CD+/− mice (n=8) after C21 injection, but C21 had no effect in WT mice (n=5). RM ANOVA CD+/−;vehicle vs CD+/−;C21 *P = 0.002. WT;vehicle vs CD+/−;vehicle *P = 0.029. Unpaired t-test WT:vehicle vs. CD+/−;C21 P = 0.574.
H. ASR is unchanged after C21 injection in WT (n=5) or CD+/− mice (n=8).
Averaged data are presented as mean ± SEM, with individual animals overlaid as lines connecting measured values in vehicle and C21.
