Fig. 1. Microbiome-centred therapies for patients with liver disease.
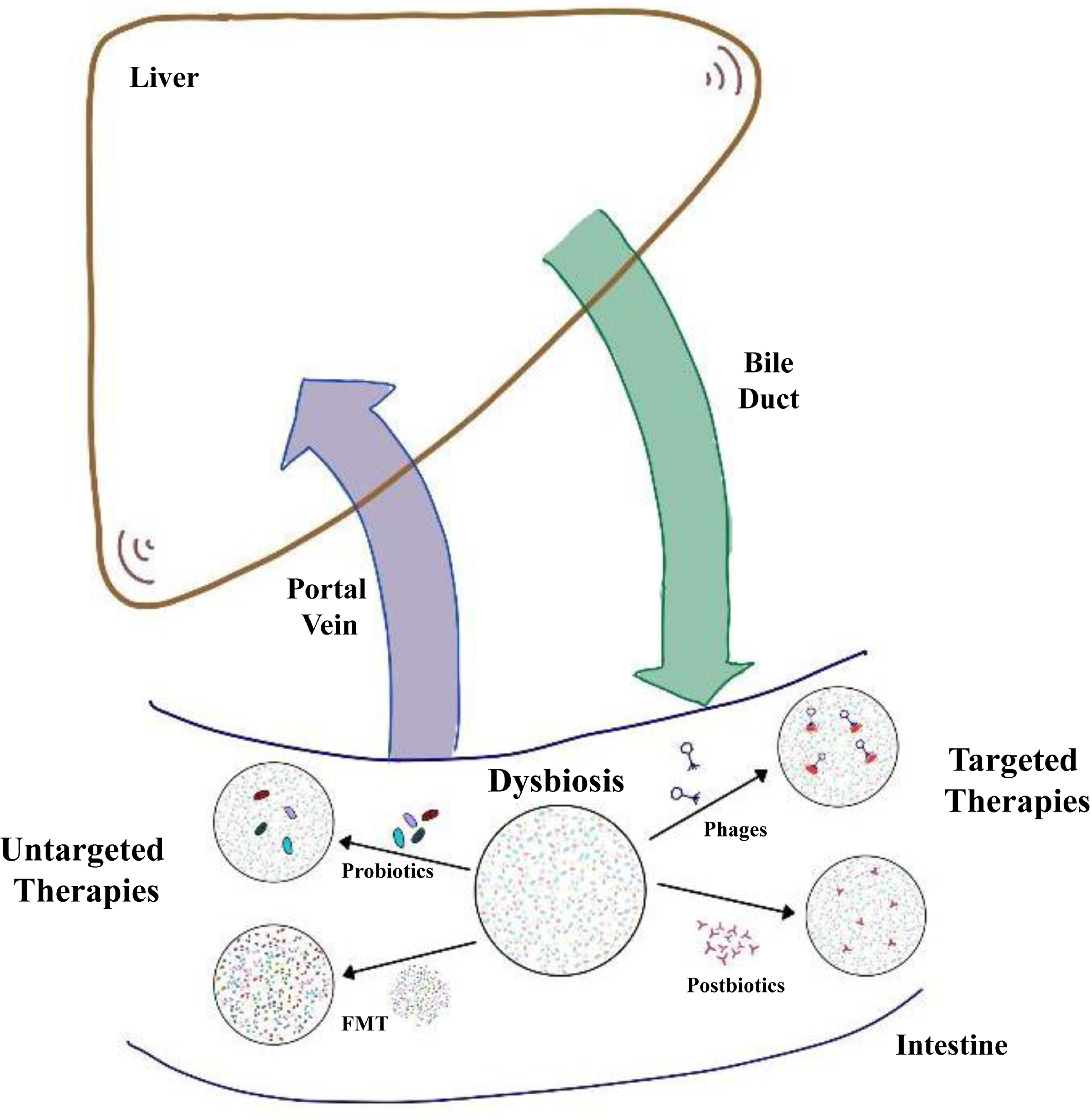
Patients with liver disease show quantitative and compositional changes in the intestinal microbiota, also called dysbiosis. Intestinal homeostasis can be restored by untargeted therapies, which include oral administration of probiotics or FMT. The aim of FMT is to replace the entire dysbiotic microbiota using stool from a healthy donor. Targeted therapies include phages and bacterial derived metabolites, also called postbiotics. Selective targeting of bacterial strains by phage therapy can modify liver disease progression in preclinical models. FMT, faecal microbiota transplant.
