Fig. 2. Engineered bacteria.
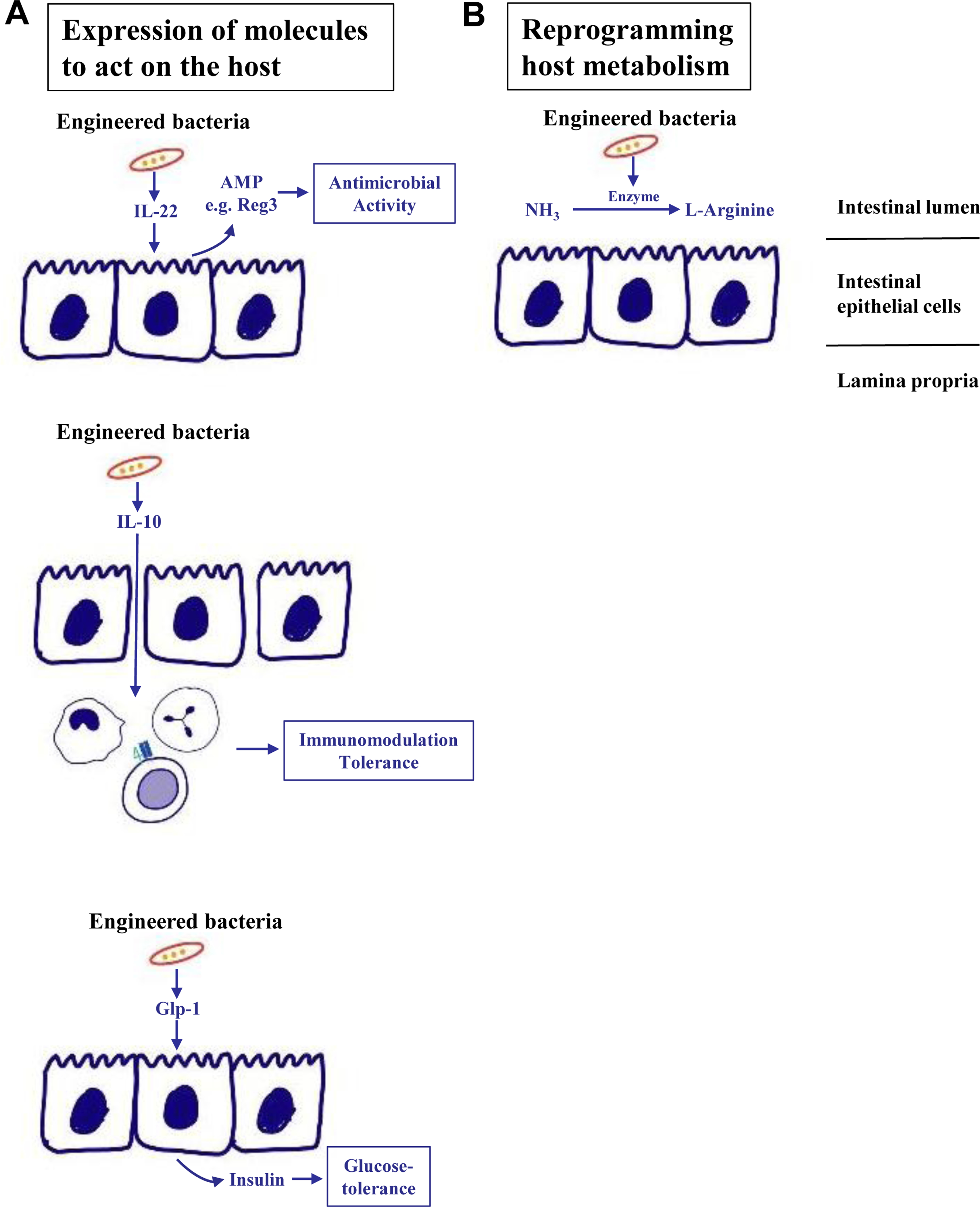
(A) Synthetic bacteria can express molecules that exert beneficial effects for the host. Examples include secretion of IL-22, which can induce AMP secretion such as Reg3 from intestinal epithelial cells to increase luminal antimicrobial activity, or IL-10, which exerts immunomodulatory and tolerogenic properties on immune cells in the lamina propria. Bacterial delivery of Glp1 induces secretion of insulin in intestinal epithelial cells to the systemic circulation and improves glucose tolerance in preclinical models. (B) In addition, engineered bacteria can metabolise toxic metabolites such as ammonia, which is converted into L-arginine. AMP, antimicrobial protein; Glp1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IL, interleukin; Reg3, regenerating islet-derived 3.
