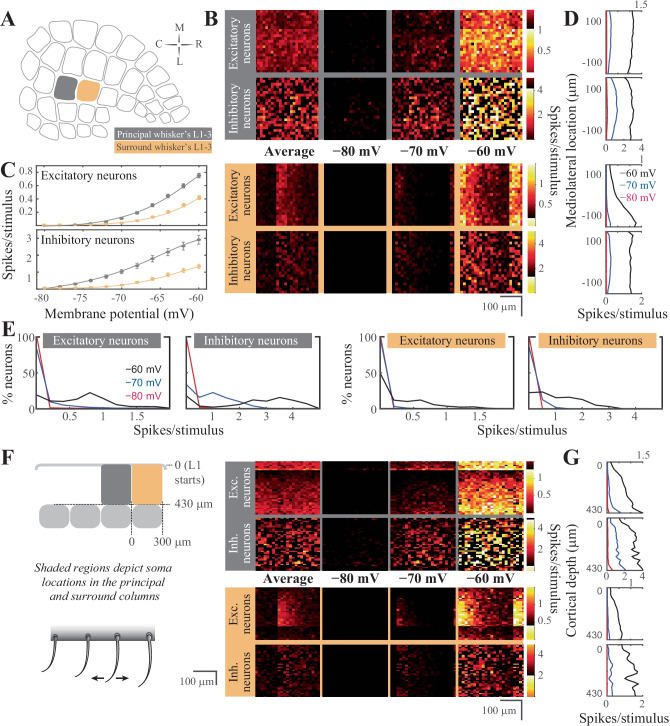
Fig. 5.
Stimulus evoked representations in the supragranular layers of the barrel cortical network in silico. (A) Schematic representation of the spatial orientation of the simulated network in the tangential plane. The principal cortical column is the D2 whisker’s column. (B) Average neuronal response mapped onto rostro-caudal (RC) and medio-lateral (ML) planes, across resting membrane states (pixel size 15 × 15 μm in cortical tissue). The figurines on the grey shaded background display the response in the principal whisker’s cortical column; yellow background shows the activity in the first order surrounding supragranular layers. (C) Average firing rate of excitatory (top) and inhibitory neurons (bottom) in the network as a function of the resting membrane potential before stimulus onset in the principal (top) and surround (bottom) whisker’s cortical network. (D) Average firing rate in the ML axis across the membrane states (i.e. each column in B was summed, then rotated 90 degrees). (E) Distribution of the spiking response per stimulus across neuron classes and membrane states. (F) Left: Schematic representation of the coronal orientation of the visualized network. Right: Average neuronal response across the dorsoventral plane in L4 (pixel size 15 × 15 μm in cortical tissue). (G) Average firing rate across cortical depth